Giant language fashions (LLMs) reminiscent of GPT-4 are thought of technological marvels able to passing the Turing check efficiently. However is that this actually the case?
ChatGPT has ascended to nice heights within the subject of synthetic intelligence (AI). It could appear good, quick and spectacular. It skillfully demonstrates seen intelligence, engages in conversations with folks, mimics human communication, and even passes exams in jurisprudence. Nonetheless, it nonetheless offers utterly false info in some instances.
So, can ChatGPT truly go the Turing check, producing textual content indistinguishable from a human response?
Two researchers from the College of California at San Diego explored this query and uncovered intriguing outcomes. Cameron Jones, who makes a speciality of language, semantics and machine studying, and Benjamin Bergen, professor of cognitive science, carried out an internet Turing check. On this check members tried to find out whether or not the respondent was an AI or a human. GPT-3.5 or GPT-4 acted as synthetic intelligence.
The experiment concerned an internet check that included conversations between 650 members and GPT fashions. Contributors had been requested to determine who they had been speaking to, a human or an AI. Numerous configurations of GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 had been used all through the experiment. For probably the most half researchers studied the immediate, which directed the LLM to a selected matter and magnificence of dialog. This immediate outlined the character of the interplay and the character of the agent, and was various to see the way it affected the end result.
Every dialogue had a 5-minute time restrict and a message size beneath 300 characters. In whole, 652 members took half within the experiment and accomplished 1810 “video games”. After filtering out doubtful outcomes, the variety of “video games” was diminished to 1,405.
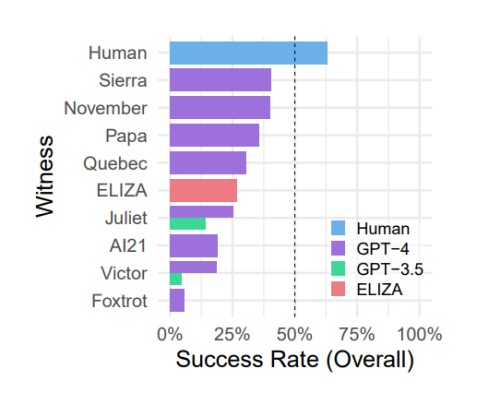
The findings revealed that the GPT-4 fashions managed to deceive members 41% of the time, whereas the GPT-3.5 fashions succeeded solely 5 – 14% of the time. For comparability, the older mannequin ELIZA (1966) was acknowledged as an individual in 27% of instances. As well as, an fascinating reality was found: members managed to persuade different members that they weren’t machines solely 63% of the time.
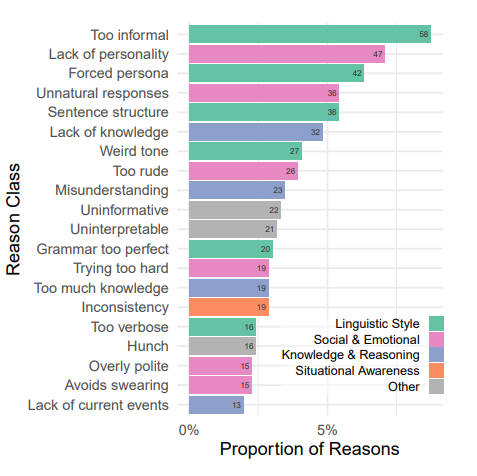
A relatively fascinating facet was the motives behind the members’ selections. The explanations AI was thought of AI had been as follows. If the AI appeared too formal or casual, it may trigger them nervousness. Equally, solutions that had been too wordy or too brief, an odd tone of dialog, or excellent grammar turned necessary components in figuring out whether or not the interlocutor was human or machine. It is usually price noting {that a} lack of understanding turned out to be extra necessary than an extra of it. This means that AI fashions ought to continue to learn. Check members additionally confirmed sensitivity to generic responses.
The researchers concluded that primarily based on this experiment, it may well’t be said that GPT-4 efficiently handed the Turing check. However, the 41% success fee signifies that the usage of AI for deception is changing into extra real looking. That is particularly related in conditions the place human interlocutors are much less attentive to the potential for speaking with a machine.
AI fashions adept at imitating human responses have the potential for far-reaching social and financial impacts. It can develop into more and more necessary to observe AI fashions and determine components that result in deception, in addition to develop methods to mitigate it. Nonetheless, the researchers emphasize that the Turing check stays an necessary software for evaluating machine dialogue and understanding human interplay with synthetic intelligence.
It is exceptional how rapidly we now have reached a stage the place technical methods can compete with people in communication. Regardless of doubts about GPT-4’s success on this check, its outcomes point out that we’re getting nearer to creating AI that may compete with people in conversations.
Learn extra concerning the research right here.

