Safety researchers have recognized a extreme pre-authentication SQL injection vulnerability in Fortinet’s FortiWeb Cloth Connector, designated as CVE-2025-25257, that permits unauthenticated attackers to execute unauthorized SQL instructions and probably obtain distant code execution.
The vulnerability impacts a number of variations of FortiWeb, together with 7.6.0 by means of 7.6.3, 7.4.0 by means of 7.4.7, 7.2.0 by means of 7.2.10, and seven.0.0 by means of 7.0.10, with patches accessible in newer variations.
FortiWeb’s Cloth Connector serves as integration middleware between FortiWeb net software firewalls and different Fortinet ecosystem merchandise, enabling dynamic safety coverage updates based mostly on real-time infrastructure adjustments and menace intelligence.
Technical Particulars of the SQL Injection Flaw
The vulnerability stems from improper enter sanitization within the get_fabric_user_by_token operate inside FortiWeb’s authentication mechanism.
Researchers found that the operate immediately incorporates user-controlled enter from HTTP Authorization headers into SQL queries with out correct validation or escaping.
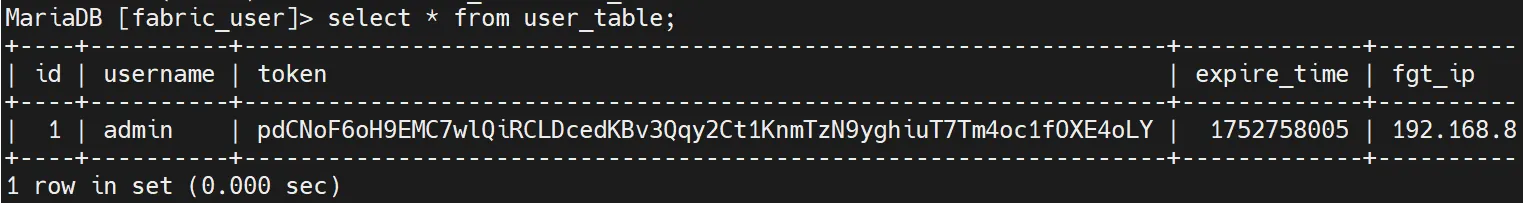
The susceptible code makes use of a format string strategy, setting up queries like choose id from fabric_user.user_table the place token='%s' the place the %s placeholder is changed with attacker-controlled information from the Authorization Bearer token.
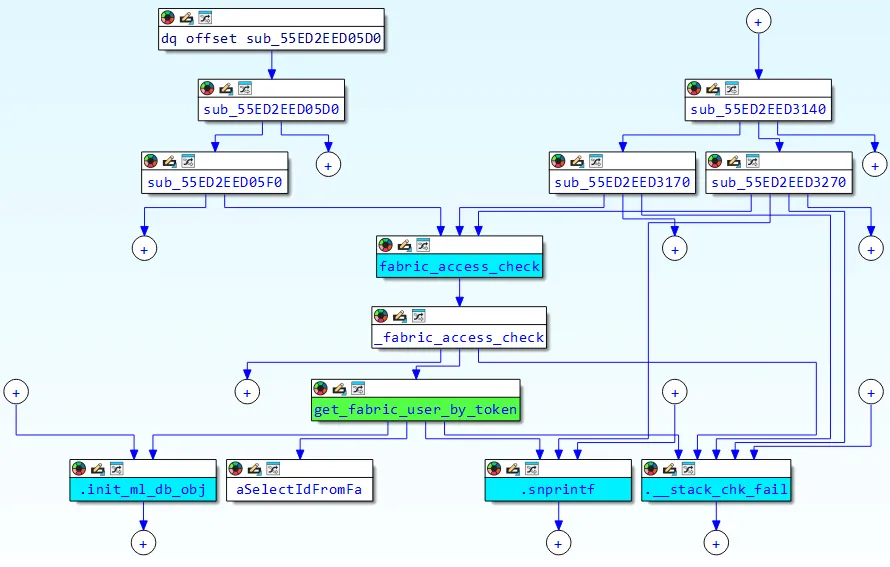
The authentication course of extracts tokens from Authorization headers utilizing the format Bearer %128s, which presents each alternatives and constraints for exploitation.
Whereas the sscanf operate limits enter to 128 characters and stops parsing on the first house character, attackers can bypass these restrictions utilizing MySQL remark syntax (/**/) to exchange areas of their injection payloads.
This permits for complicated SQL injection assaults regardless of the obvious enter limitations.
Fortinet has addressed the vulnerability in patched variations by changing the susceptible format string queries with ready statements utilizing MySQL’s mysql_stmt_prepare operate.
The up to date implementation makes use of parameterized queries with placeholders (SELECT id FROM fabric_user.user_table WHERE token = ?) that correctly separate SQL code from consumer information, stopping injection assaults.
Escalation from SQL Injection to Distant Code Execution
Safety researchers demonstrated how this SQL injection vulnerability may be escalated to realize full distant code execution by means of a classy assault chain.
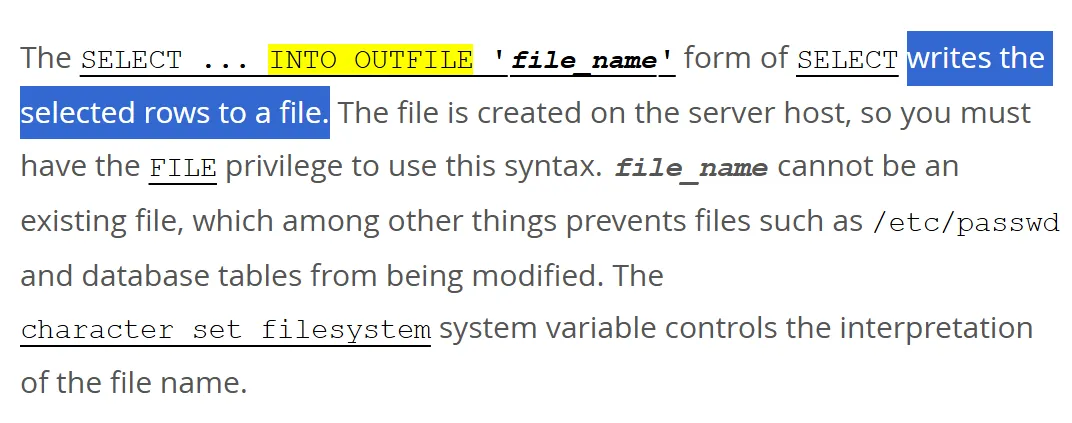
The exploitation leverages MySQL’s INTO OUTFILE assertion to write down arbitrary information to the goal system, mixed with Python’s site-specific configuration hooks for code execution.
Key steps within the assault chain embody:
- Utilizing SQL injection to write down a malicious
.pthfile into Python’s site-packages listing. - Crafting payloads utilizing MySQL’s
UNHEX()operate to sidestep character restrictions. - Storing code in database columns after which dumping the contents through
INTO OUTFILEwith relative file paths. - Triggering Python code execution by accessing the uncovered
/cgi-bin/ml-draw.pyscript, which masses the malicious.pthfile as a part of its startup routine.
This exploitation chain bypasses a number of system restrictions and demonstrates how a easy injection can quickly escalate right into a full compromise of the affected system.
Organizations working affected FortiWeb variations ought to instantly implement detection measures and apply accessible patches.
The vulnerability may be detected by monitoring for particular HTTP requests to fabric-related API endpoints, significantly /api/material/system/standing, /api/material/authenticate, and /api/v[0-9]/material/widget paths.
Safety groups ought to look ahead to Authorization headers containing SQL injection indicators akin to single quotes, MySQL remark syntax (/**/), or boolean logic statements like 'or'1'='1.
Profitable exploitation makes an attempt sometimes return HTTP 200 responses with JSON information containing system info, whereas failed makes an attempt on patched techniques return HTTP 401 Unauthorized responses.
Fortinet has launched patches for all affected variations, with customers suggested to improve to FortiWeb 7.6.4 or above, 7.4.8 or above, 7.2.11 or above, or 7.0.11 or above relying on their present deployment.
As an instantaneous mitigation, organizations can limit entry to material API endpoints till patches are utilized, although this may occasionally affect respectable integration performance with different Fortinet merchandise.
Keep Up to date on Day by day Cybersecurity Information. Comply with us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X.

