JFrog Safety Analysis has uncovered three essential zero-day vulnerabilities in PickleScan, a widely-adopted industry-standard instrument for scanning machine studying fashions and detecting malicious content material.
These vulnerabilities would allow attackers to fully bypass PickleScan’s malware detection mechanisms, probably facilitating large-scale provide chain assaults by distributing malicious ML fashions containing undetectable code.
The discoveries underscore a basic weak point within the AI safety ecosystem’s reliance on a single safety answer.
PyTorch’s recognition in machine studying comes with a big safety burden. The library hosts over 200,000 publicly out there fashions on platforms like Hugging Face, but it depends on Python’s “pickle” serialization format by default.
Whereas pickle’s flexibility permits for reconstructing any Python object, this similar attribute creates a essential vulnerability: pickle information can embed and execute arbitrary Python code throughout deserialization.
When customers load an untrusted PyTorch mannequin, they threat executing malicious code able to exfiltrating delicate information, putting in backdoors, or compromising total programs.
This menace isn’t theoretical malicious fashions have already been found on Hugging Face, concentrating on unsuspecting information scientists with silent backdoors.
PickleScan emerged because the {industry}’s frontline protection, parsing pickle bytecode to detect harmful operations earlier than execution.
The instrument analyzes information on the bytecode degree, cross-references outcomes towards a blocklist of hazardous imports, and helps a number of PyTorch codecs.
Nevertheless, its safety mannequin rests on a essential assumption: PickleScan should interpret information identically to how PyTorch hundreds them. Any divergence in parsing creates exploitable safety gaps.
Three Important Vulnerabilities
The primary vulnerability (CVE-2025-10155, CVSS 9.3) exploits PickleScan’s file kind detection logic.
By renaming a malicious pickle file with a PyTorch-related extension like .bin or .pt, attackers could cause PickleScan’s PyTorch-specific scanner to fail whereas PyTorch itself efficiently hundreds the file by analyzing its content material slightly than its extension. The malicious payload executes undetected.
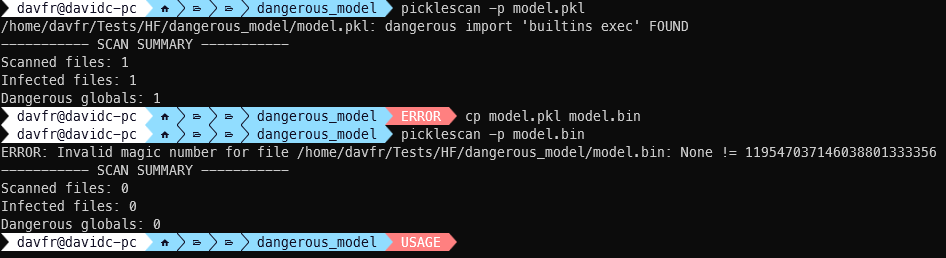
The second vulnerability (CVE-2025-10156, CVSS 9.3) entails CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Test) errors in ZIP archives.
PickleScan fails fully when encountering CRC mismatches, elevating exceptions that halt scanning.
Nevertheless, PyTorch’s mannequin loading typically bypasses these CRC checks, making a harmful discrepancy the place PickleScan marks information as unscanned whereas PyTorch hundreds and executes their contents efficiently.
The third vulnerability (CVE-2025-10157, CVSS 9.3) reveals that PickleScan’s unsafe globals test could be circumvented through the use of subclasses of harmful imports slightly than actual module names.
For example, importing inside lessons from asyncio a blacklisted library bypasses the test totally, permitting attackers to inject malicious payloads whereas PickleScan categorizes the menace as merely “suspicious” slightly than “harmful.”
Systemic Safety Implications
These vulnerabilities expose deeper issues in AI safety infrastructure. The ecosystem’s single level of failure round PickleScan implies that when the instrument fails, total safety architectures collapse.
Organizations counting on Hugging Face, which integrates PickleScan for scanning thousands and thousands of uploaded fashions, face explicit threat.
The vulnerabilities show how divergences between safety instruments and goal functions create exploitable gaps a essential lesson for AI safety professionals.
Organizations ought to instantly replace to PickleScan model 0.0.31, which addresses all three vulnerabilities.
Nevertheless, this patch alone is inadequate. Implementing layered defenses together with sandboxed environments and safe mannequin repository proxies like JFrog Artifactory gives further safety.
Organizations ought to prioritize migrating to safer ML mannequin codecs akin to Safetensors whereas implementing automated elimination of failed safety scans.
The AI safety group should acknowledge that no single instrument can assure complete safety and that defense-in-depth methods stay important on this evolving menace panorama.
Observe us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X to Get Instantaneous Updates and Set GBH as a Most well-liked Supply in Google.

