Know-how could also be altering quickly however one factor stays fixed: It’s not a simple time to be a CSO. The function continues to evolve with safety leaders taking over much more tasks, and 76% reporting that understanding which safety options greatest match their firm has grown extra advanced, based on CSO’s 2025 Safety Priorities Examine.
Additional, 57% of respondents report their group has struggled to seek out the basis reason behind safety incidents they skilled prior to now yr.
Nowadays, safety leaders discover themselves tasked with a spread of high-level tasks, together with cyber technique and coverage growth, threat administration, and managing the dangers of AI-enabled expertise. Furthermore, 67% of safety leaders say their tasks require them to handle safety points exterior their nation or area.
Holding them again are perennial issues: worker consciousness coaching; lack of finances; retaining certified workers; course of complexity; and, more and more, the power to handle the dangers offered by disruptive applied sciences equivalent to AI.
Defending information continues to be a key precedence
Based on CSO’s survey, safety leaders have a number of key areas of focus, together with strengthening safety of confidential and delicate information (48%), securing cloud information and techniques (45%), and simplifying IT safety infrastructure (39%).
CSO
Zach Lewis, CIO and CISO of College of Well being Sciences & Pharmacy in St. Louis, says consolidating instruments and utilizing what they’ve extra totally are his primary priorities going into subsequent yr. “We’re shifting extra within the path of platforms as a substitute of better of breed to attempt to discover some price financial savings and simplify the tech stack,’’ Lewis says.
Moreover, the college’s information governance journey continues. “We have now managed to categorise and categorize our information,’’ he says. “Now we’re locking that information into our retention interval coverage and cleansing up duplicate information.”
AI plans range
AI continues to penetrate deeper into the enterprise, together with the safety operations heart. Seventy-three % of safety decision-makers are extra probably this yr to contemplate a safety answer that makes use of AI, up from 59% in 2024, and 58% plan to extend spending on AI-enabled safety expertise, based on the CSO survey.
Keavy Murphy, vice chairman of safety at Internet Well being, is giving appreciable thought to AI’s affect and the way the group goes to navigate the expertise heading into 2026.
“This yr, it turned abundantly clear that AI isn’t going wherever. The truth is, it’s changing into extra integral than ever, even in industries like healthcare which have traditionally been thought-about laggards,’’ Murphy says. In a current survey of healthcare leaders Internet Well being participated in, 93% of respondents indicated their organizations are prioritizing AI adoption for medical resolution help within the subsequent 12 to 24 months, she says.
The identical survey revealed that confidence in AI continues to be forming, and adoption will rely on whether or not these instruments show adequate ROI, ease of use, and regulatory security, Murphy notes. Whereas she is “in full help of this degree of AI adoption,” Murphy acknowledges that this “is perhaps an uncommon take from a cybersecurity professional, since many people are cautious of superior applied sciences which may open us as much as menace.’’
Murphy causes that since “there’s no query that dangerous actors might be utilizing AI and essentially the most superior software program doable of their assaults,’’ organizations which might be prone to those assaults, like hospitals or personal practices, should reply with equally refined instruments.
“I believe AI is an unbelievable innovation that may assist healthcare organizations streamline so a lot of their day-to-day operations like documentation, administrative duties, and extra,’’ she explains. “It’s solely proper that we make the most of it for cybersecurity functions, as nicely.”
AI is already occasion of cyber threat planning at Aflac, says Tim Callahan, international CISO, who expects its utilization will solely improve in 2026. Already, his group is leveraging AI and machine studying for menace detection and response in addition to malware identification.
“Moreover, AI can also be serving to us automate repetitive duties, triage alerts, and prioritize vulnerabilities, however by no means on the expense of a hands-on method the place professional analysis and intelligence is vital,’’ Callahan stresses. “Because the world’s adversaries launch extra refined AI-driven assaults, it’s vital that we use these applied sciences to not solely maintain tempo however keep forward.”
He says management is rigorously evaluating AI’s function at Aflac and inside the cybersecurity groups, “particularly as regulatory frameworks adapt to new applied sciences.”
Lewis of College of Well being Sciences & Pharmacy shouldn’t be as gung-ho on AI, saying it is not going to play a big function in his cyber threat planning. Whereas issues like phishing emails, video deepfakes, voice fakes, and faux photos are a priority, “foundationally, lots of issues nonetheless maintain,’’ he says. “I’m not pouring a ton of funding into that; simply reinforcing these … safety stack items that I have already got in place and ensuring that customers are conscious and that our techniques are tuned correctly.”
Concern over AI-enabled assaults rises
Like Internet Well being’s Murphy, safety patrons are involved about AI-enabled cyberattacks.
Particularly, 38% of respondents expressed fear about AI-enabled ransomware, whereas safety leaders additionally cited attackers leveraging AI to facilitate assault automation (35%) and an adversary’s use of AI to hunt for vulnerabilities of their enterprise (33%) as different high AI-related considerations.
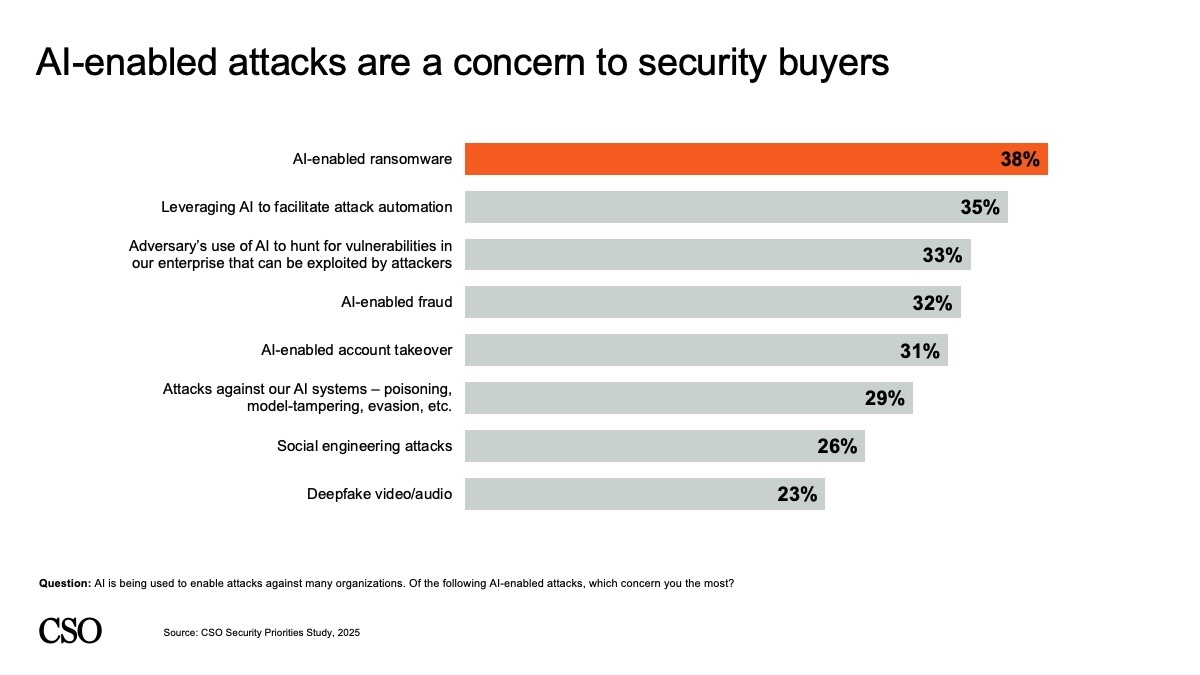
CSO
Consequently, 41% are planning to leverage AI to detect threats, for anomaly detection, and to automate safety responses. Different respondents cited plans to leverage AI for malware detection and real-time threat prediction (39%), in addition to DLP and enhancing enterprise system visibility.
Additional, 40% count on to see AI enhancements as a part of their current safety techniques — with out further expenses — whereas 32% are prepared to pay a premium for AI-enabled safety options that meet their particular safety wants.
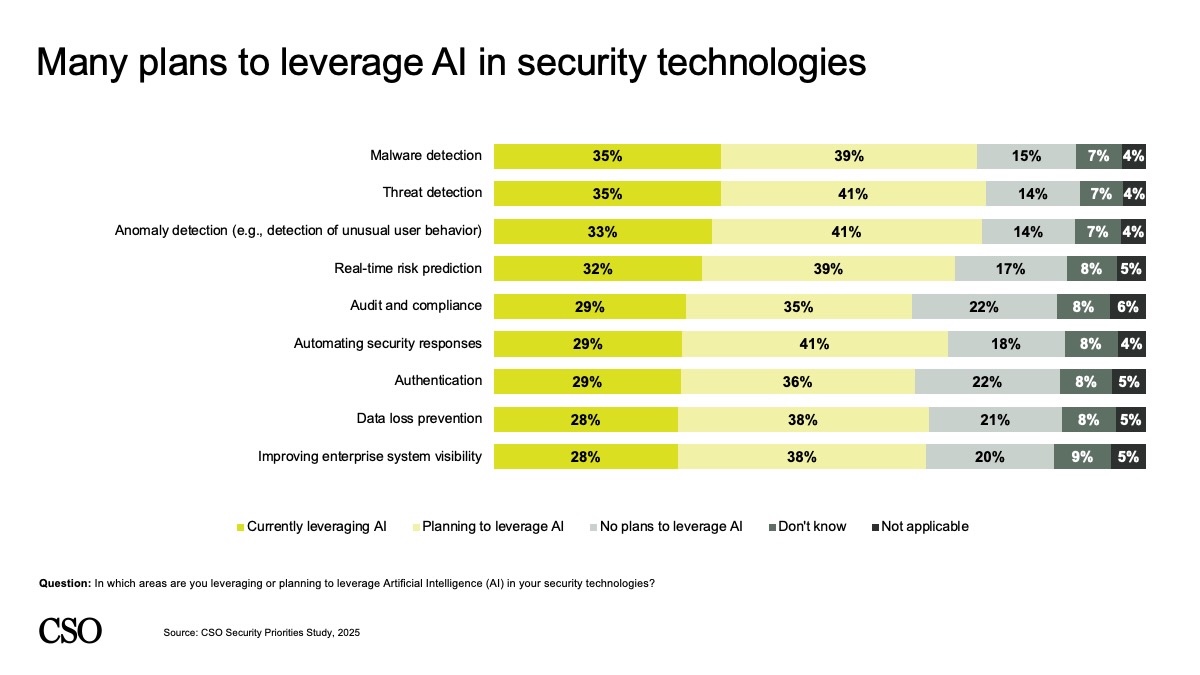
CSO
The advantages AI safety tech offers
A whopping 99% of respondents have already seen advantages from the AI-enabled safety applied sciences, up from 72% in 2023.
Among the many advantages: quicker identification of unknown threats (44%), accelerated detection and response occasions (42%), the power to sift via massive quantities of information quicker(42%), lowered worker workloads because of automation (42%), and the power of to be extra proactive (42%).
Instrument priorities for a shifting menace panorama
Safety leaders report a variety of instruments in manufacturing, together with options for authentication (36%), safety consciousness and coaching (35%), incident response (34%), DLP (33%), and EDR (32%).
Instruments on their radar embrace safety analytics (28%), enterprise safety administration (27%), SIEM (26%), and information governance (26%).
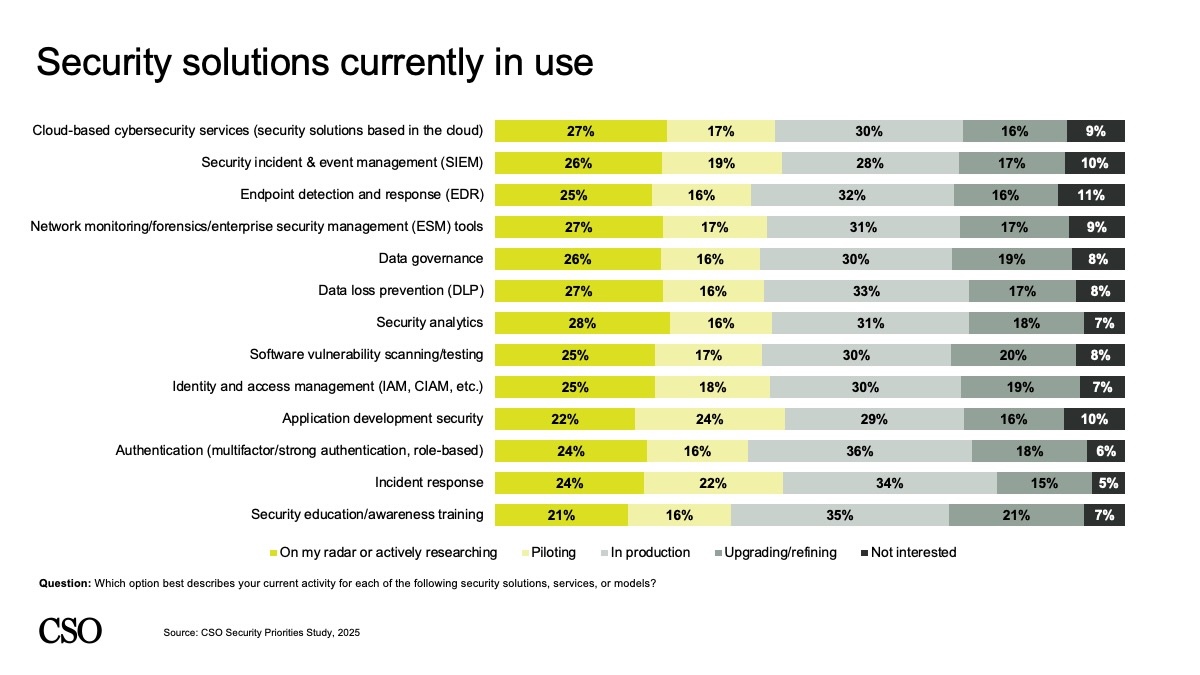
CSO
Aflac’s Callahan says his group is prioritizing “extremely advanced safety instruments.’’ For instance, the corporate took a personalized method when implementing zero belief, together with entry detection and blocking, he says. “This method has helped us keep away from errors and pitfalls that might affect our enterprise,’’ Callahan says.
Subsequent yr, the plan is to implement instruments “that improve visibility and supply higher automation and integration throughout our surroundings,” he provides.
The College of Well being Sciences & Pharmacy lately added a brand new DLP instrument that’s nonetheless in stealth mode, which “comes again to the AI considerations,’’ Lewis says.
He’s additionally planning to consolidate a few instruments centered on e mail safety and using Microsoft’s e mail gateway and different safety items, because the college is a Microsoft store. That may give him the power to buy the DLP system, “which is essential, as our information is now going into extra AI techniques,” he says. “I need to be certain I’m maintaining a tally of that and ensuring delicate and proprietary information or analysis isn’t slipping away into these public LLMs.”
Budgets will stay comparatively unchanged
Some 55% of respondents stated their safety budgets will stay the identical, whereas 43% report anticipating a rise, based on the Safety Priorities survey.
Lewis anticipates degree funding subsequent yr, with a doable 1% improve, which is par for the course in larger ed, he says. “I’ll make do with the instruments I’ve,’’ he says.
Any will increase to Callahan’s finances at Aflac “might be pushed by the necessity to put money into superior applied sciences, ways to handle rising regulatory necessities, and the continuing want for expertise growth,” he says.
Survey respondents reported the primary enterprise priorities driving safety spending to be: rising cybersecurity protections (42%), rising operational effectivity (37%), accelerating AI-driven innovation and purposes (31%), enhancing profitability (30%), and remodeling current enterprise processes equivalent to automation and integration (30%).
MSPs retain their worth because the safety panorama grows extra advanced
One other discovering on this yr’s survey is that 90% of respondents plan to outsource safety capabilities to a managed companies supplier (MSP) or different third-party supplier within the subsequent yr.
Aflac has been using managed safety service suppliers (MSSPs) for years, significantly to supply 24/7 protection, Callahan says.
“In 2026, we are going to proceed to increase our partnerships with third-party suppliers, although to not exchange our core group, however somewhat to reinforce our group’s outputs round strategic initiatives,’’ he says. “Because the surroundings grows extra advanced, we count on to see further help in areas equivalent to vulnerability administration and compliance.”
Lewis echoes that, saying the college will proceed to make use of third-party suppliers to have 24/7 SOC protection. His MSSP can also be dealing with SIEM, logging occasions, and EDR.
CSOs’ visibility is on the rise
As their tasks improve, safety leaders are gaining the eye of their boards — 95% reported they interact with their board of administrators, up from 85% in 2023. Forty-eight % interact with their board a number of occasions a month.
Moreover, 70% of respondents report that somebody on their group’s board of administrators has particular duty or oversight for cybersecurity, up from 59% in 2024. Seventy-two % stated engagement with their board has helped enhance cybersecurity/safety initiatives, up from 66% in 2024.
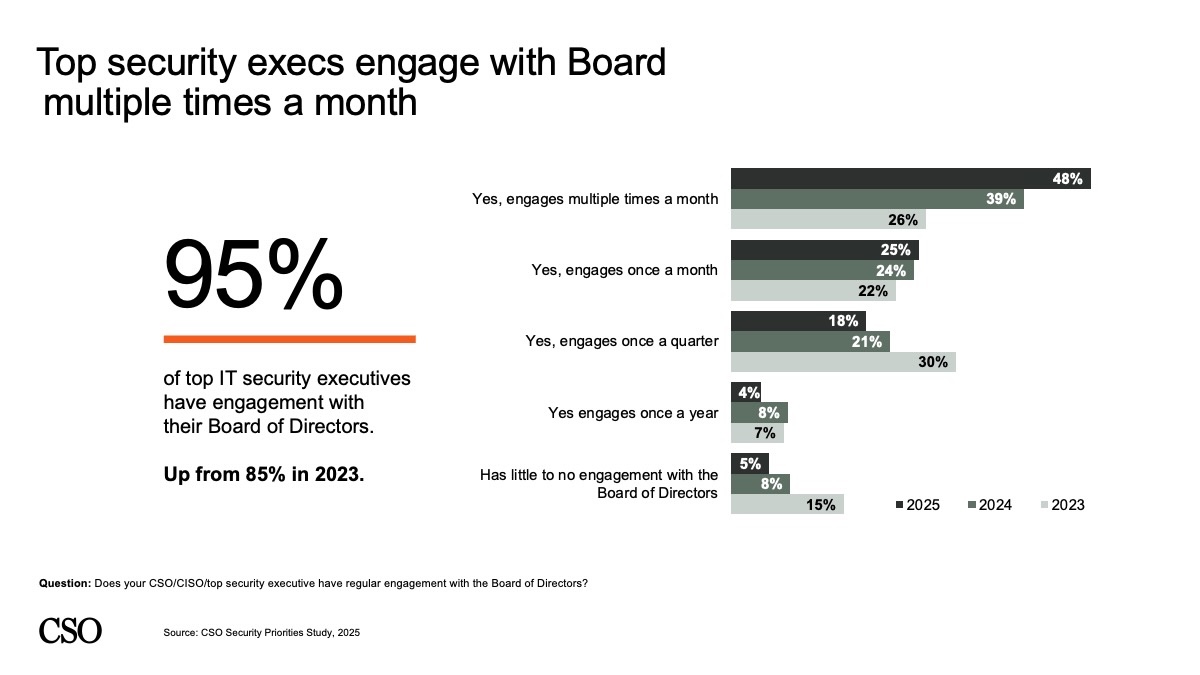
CSO
Lewis meets with the college’s board or audit committee nearly quarterly, and he thinks that’s enough.
“I believe lots of CISOs actually suppose they want a seat at desk,’’ which can be organization- or industry-specific, he says. However he believes safety leaders must as a substitute work on having a greater relationship with their CEO.
CISOs must be “working to safe issues extra internally than essentially what’s occurred externally, and having that relationship with the manager group [and] different useful leaders within the group,’’ he says. That, Lewis provides, is “arguably extra necessary than essentially having a seat on the board desk.”
CSO’s Safety Priorities Report surveyed 641 respondents to realize a greater understanding of the assorted safety tasks organizations are centered on now and within the coming yr. The analysis additionally checked out points that may demand essentially the most time and strategic pondering for IT and safety groups. Respondents got here from North America (46%), APAC (36%), and EMEA (18%). The common firm dimension is 14,494 workers.

