This text exhibits how Shannon’s info principle connects to the instruments you’ll discover in trendy machine studying. We’ll handle entropy and data achieve, then transfer to cross-entropy, KL divergence, and the strategies utilized in as we speak’s generative studying programs.
Right here’s what’s forward:
- Shannon’s core thought of quantifying info and uncertainty (bits) and why uncommon occasions carry extra info
- The development from entropy → info achieve/mutual info → cross-entropy and KL divergence
- How these concepts present up in follow: choice bushes, characteristic choice, classification losses, variational strategies, and InfoGAN
From Shannon to Fashionable AI: A Full Data Concept Information for Machine Studying
Picture by Creator
In 1948, Claude Shannon revealed a paper that modified how we take into consideration info ceaselessly. His mathematical framework for quantifying uncertainty and shock turned the inspiration for every part from knowledge compression to the loss features that practice as we speak’s neural networks.
Data principle provides you the mathematical instruments to measure and work with uncertainty in knowledge. When you choose options for a mannequin, optimize a neural community, or construct a choice tree, you’re making use of ideas Shannon developed over 75 years in the past. This information connects Shannon’s unique insights to the knowledge principle ideas you utilize in machine studying as we speak.
What Shannon Found
Shannon’s breakthrough was to deal with info as one thing you would really measure. Earlier than 1948, info was qualitative — you both had it otherwise you didn’t. Shannon confirmed that info might be quantified mathematically by taking a look at uncertainty and shock.
The elemental precept is elegant: uncommon occasions carry extra info than widespread occasions. Studying that it rained within the desert tells you greater than studying the solar rose this morning. This relationship between chance and data content material turned the inspiration for measuring uncertainty in knowledge.
Shannon captured this relationship in a easy mathematical system:
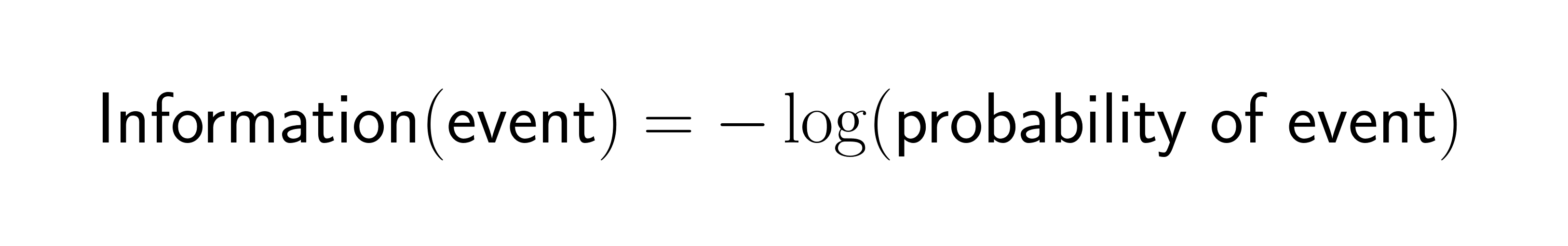
When an occasion has chance 1.0 (certainty), it provides you zero info. When an occasion is extraordinarily uncommon, it offers excessive info content material. This inverse relationship drives most info principle functions in machine studying.
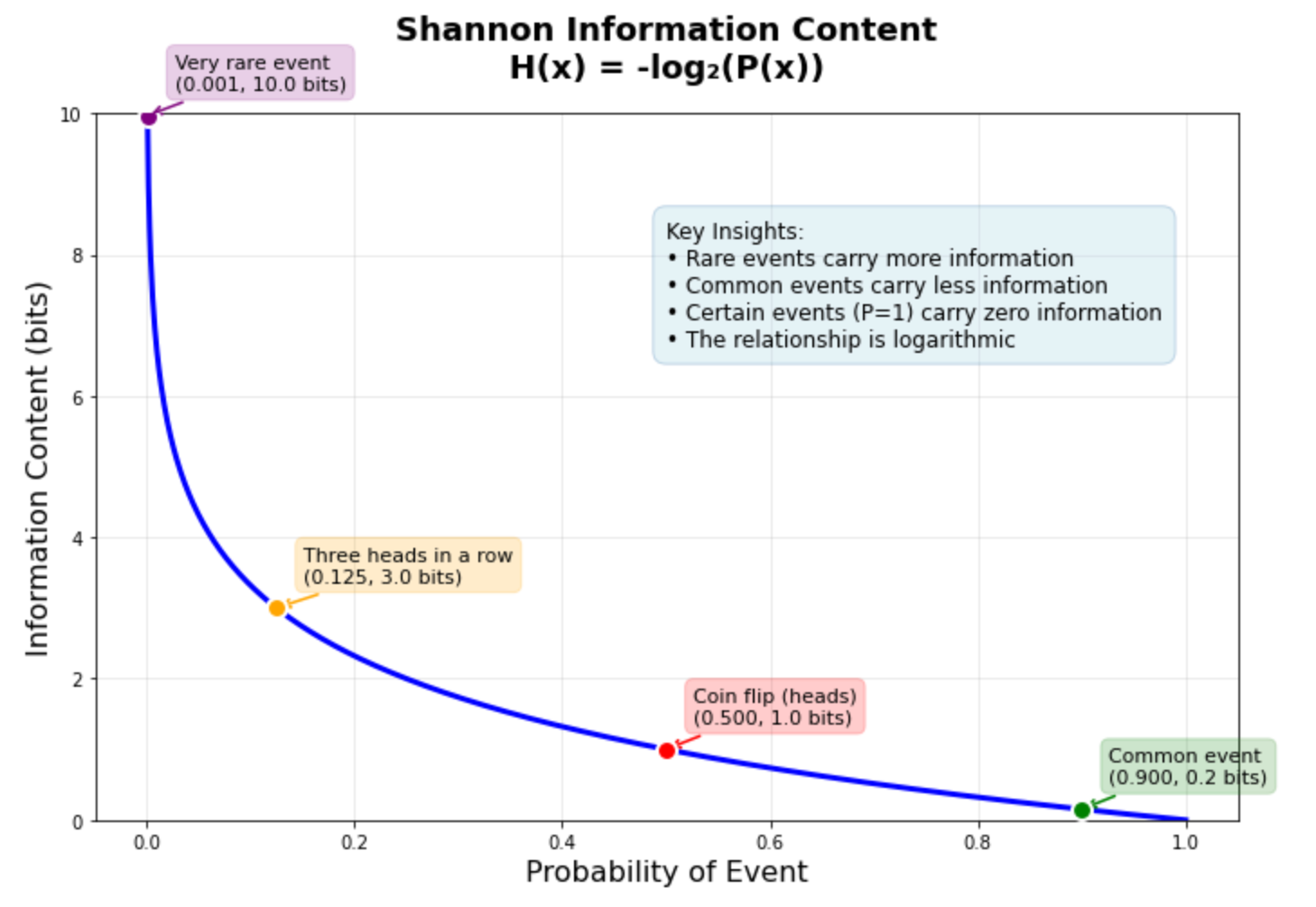
The graph above exhibits this relationship in motion. A coin flip (50% chance) carries precisely 1 bit of knowledge. Getting three heads in a row (12.5% chance) carries 3 bits. A really uncommon occasion with 0.1% chance carries about 10 bits — roughly ten occasions extra info than the coin flip. This logarithmic relationship helps clarify why machine studying fashions typically wrestle with uncommon occasions: they carry a lot info that the mannequin wants many examples to be taught dependable patterns.
Constructing the Mathematical Basis: Entropy
Shannon prolonged his info idea to complete chance distributions by entropy. Entropy measures the anticipated info content material when sampling from a chance distribution.
For a distribution with equally doubtless outcomes, entropy reaches its most — there’s excessive uncertainty about which occasion will happen. For skewed distributions the place one consequence dominates, entropy is decrease as a result of the dominant consequence is predictable.
This is applicable on to machine studying datasets. A superbly balanced binary classification dataset has most entropy, whereas an imbalanced dataset has decrease entropy as a result of one class is extra predictable than the opposite.
For the entire mathematical derivation, step-by-step calculations, and Python implementations, see A Mild Introduction to Data Entropy. This tutorial offers labored examples and implementations from scratch.
From Entropy to Data Achieve
Shannon’s entropy idea leads naturally to info achieve, which measures how a lot uncertainty decreases whenever you be taught one thing new. Data achieve calculates the discount in entropy whenever you cut up knowledge in accordance with some criterion.
This precept drives choice tree algorithms. When constructing a choice tree, algorithms like ID3 and CART consider potential splits by calculating info achieve. The cut up that offers you the largest discount in uncertainty will get chosen.
Data achieve additionally extends to characteristic choice by mutual info. Mutual info measures how a lot understanding one variable tells you about one other variable. Options with excessive mutual info relative to the goal variable are extra informative for prediction duties.
The mathematical relationship between entropy, info achieve, and mutual info, together with labored examples and Python code, is defined intimately in Data Achieve and Mutual Data for Machine Studying. This tutorial offers step-by-step calculations displaying precisely how info achieve guides choice tree splitting.
Cross-Entropy As a Loss Operate
Shannon’s info principle ideas discovered direct utility in machine studying by cross-entropy loss features. Cross-entropy measures the distinction between predicted chance distributions and true distributions.
When coaching classification fashions, cross-entropy loss quantifies how a lot info is misplaced when utilizing predicted possibilities as an alternative of true possibilities. Fashions that predict chance distributions nearer to the true distribution have decrease cross-entropy loss.
This connection between info principle and loss features isn’t coincidental. Cross-entropy loss emerges naturally from most chance estimation, which seeks to search out mannequin parameters that make the noticed knowledge most possible underneath the mannequin.
Cross-entropy turned the usual loss operate for classification duties as a result of it offers sturdy gradients when predictions are assured however flawed, serving to fashions be taught quicker. The mathematical foundations, implementation particulars, and relationship to info principle are lined completely in A Mild Introduction to Cross-Entropy for Machine Studying.
Measuring Distribution Variations: KL Divergence
Constructing on cross-entropy ideas, the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence provides you a technique to measure how a lot one chance distribution differs from one other. KL divergence quantifies the extra info wanted to signify knowledge utilizing an approximate distribution as an alternative of the true distribution.
Not like cross-entropy, which measures coding value relative to the true distribution, KL divergence measures the additional info value of utilizing an imperfect mannequin. This makes KL divergence notably helpful for evaluating fashions or measuring how effectively one distribution approximates one other.
KL divergence seems all through machine studying in variational inference, generative fashions, and regularization strategies. It offers a principled technique to penalize fashions that deviate too removed from prior beliefs or reference distributions.
The mathematical foundations of KL divergence, its relationship to cross-entropy and entropy, plus implementation examples are detailed in Learn how to Calculate the KL Divergence for Machine Studying. This tutorial additionally covers the associated Jensen-Shannon divergence and exhibits learn how to implement each measures in Python.
Data Concept in Fashionable AI
Fashionable AI functions lengthen Shannon’s ideas in refined methods. Generative adversarial networks (GANs) use info principle ideas to be taught knowledge distributions, with discriminators performing information-theoretic comparisons between actual and generated knowledge.
The Data Maximizing GAN (InfoGAN) explicitly incorporates mutual info into the coaching goal. By maximizing mutual info between latent codes and generated photographs, InfoGAN learns disentangled representations the place totally different latent variables management totally different points of generated photographs.
Transformer architectures, the inspiration of contemporary language fashions, might be understood by info principle lenses. Consideration mechanisms route info primarily based on relevance, and the coaching course of learns to compress and remodel info throughout layers.
Data bottleneck principle offers one other trendy perspective, suggesting that neural networks be taught by compressing inputs whereas preserving info related to the duty. This view helps clarify why deep networks generalize effectively regardless of their excessive capability.
An entire implementation of InfoGAN with detailed explanations of how mutual info is included into GAN coaching is offered in Learn how to Develop an Data Maximizing GAN (InfoGAN) in Keras.
Constructing Your Data Concept Toolkit
Understanding when to use totally different info principle ideas improves your machine studying follow. Right here’s a framework for choosing the proper device:
Use entropy when you must measure uncertainty in a single distribution. This helps consider dataset stability, assess prediction confidence, or design regularization phrases that encourage numerous outputs.
Use info achieve or mutual info when deciding on options or constructing choice bushes. These measures establish which variables provide the most details about your goal variable.
Use cross-entropy when coaching classification fashions. Cross-entropy loss offers good gradients and connects on to most chance estimation ideas.
Use KL divergence when evaluating chance distributions or implementing variational strategies. KL divergence measures distribution variations in a principled manner that respects the probabilistic construction of your downside.
Use superior functions like InfoGAN when you must be taught structured representations or need specific management over info movement in generative fashions.
This development strikes from measuring uncertainty in knowledge (entropy) to optimizing fashions (cross-entropy). Superior functions embrace evaluating distributions (KL divergence) and studying structured representations (InfoGAN).
Subsequent Steps
The 5 tutorials linked all through this information present complete protection of knowledge principle for machine studying. They progress from primary entropy ideas by functions to superior strategies like InfoGAN.
Begin with the entropy tutorial to construct instinct for info content material and uncertainty measurement. Transfer by info achieve and mutual info to grasp characteristic choice and choice bushes. Examine cross-entropy to grasp trendy loss features, then discover KL divergence for distribution comparisons. Lastly, look at InfoGAN to see how info principle ideas apply to generative fashions.
Every tutorial contains full Python implementations, labored examples, and functions. Collectively, they offer you a whole basis for making use of info principle ideas in your machine studying initiatives.
Shannon’s 1948 insights proceed to drive improvements in synthetic intelligence. Understanding these ideas and their trendy functions provides you entry to a mathematical framework that explains why many machine studying strategies work and learn how to apply them extra successfully.

