Safety researchers have found crucial privilege escalation vulnerabilities in Google’s Vertex AI platform that permit attackers with minimal permissions to hijack high-privileged Service Agent accounts.
The issues have an effect on the Vertex AI Agent Engine and Ray on Vertex AI, the place default configurations allow low-privileged customers to entry highly effective managed identities with project-wide permissions.
As enterprises quickly deploy Generative AI infrastructure, with 98% at the moment experimenting or implementing platforms like Google Cloud Vertex AI, these ignored id dangers pose important threats to cloud environments.
Service Brokers are particular service accounts managed by Google Cloud that carry out inner operations on behalf of customers, typically receiving broad permissions routinely.
Researchers recognized two distinct assault vectors that rework these “invisible” managed identities into exploitable privilege escalation pathways.
When disclosed to Google, the corporate responded that the companies are “working as supposed,” which means these configurations stay the default as we speak.
Platform engineers and safety groups should perceive these technical mechanics to safe their environments instantly.
The primary vulnerability targets the Vertex AI Agent Engine, which permits builders to deploy AI brokers on GCP infrastructure utilizing frameworks resembling Google’s ADK.
| Function | Vertex AI Agent Engine | Ray on Vertex AI |
|---|---|---|
| Main Goal | Reasoning Engine Service Agent | Customized Code Service Agent |
| Vulnerability Kind | Malicious Device Name (RCE) | Insecure Default Entry (Viewer to Root) |
| Preliminary Permission | aiplatform.reasoningEngines.replace | aiplatform.persistentResources.get/listing |
| Impression | LLM recollections, chats, GCS entry | Ray cluster root; BigQuery/GCS R/W |
Researchers found that attackers with aiplatform.reasoningEngines.Replace permission can inject malicious Python code into software calls inside reasoning engines.
The assault works by updating an current reasoning engine with a software containing malicious code, resembling a reverse shell embedded inside a regular perform.
When triggered, the code executes on the reasoning engine’s compute occasion, permitting attackers to extract credentials for the “Reasoning Engine Service Agent” via the occasion metadata service.
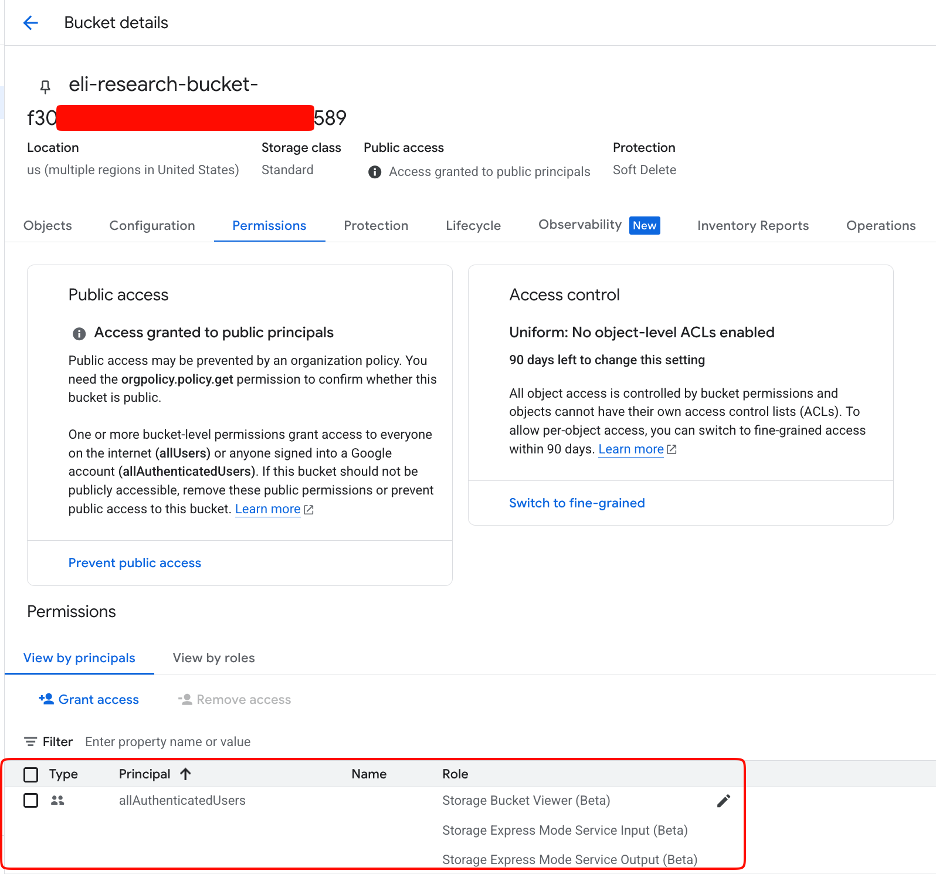
By default, this service agent possesses intensive permissions, together with entry to Vertex AI recollections, chat classes, storage buckets, and logging capabilities.
Attackers can learn all chat conversations, entry LLM recollections, and retrieve delicate info from storage assets.
Critically, the assault requires solely minimal permissions, as public buckets from any account can function staging areas.
Ray on Vertex AI
The second vulnerability impacts Ray on Vertex AI clusters, the place the “Customized Code Service Agent” routinely attaches to cluster head nodes.
Researchers from XM Cyber found that customers with solely aiplatform.persistentResources.listing and aiplatform.persistentResources.
These with permissions included in the usual “Vertex AI Viewer” function can acquire root entry to go nodes by way of the GCP Console.
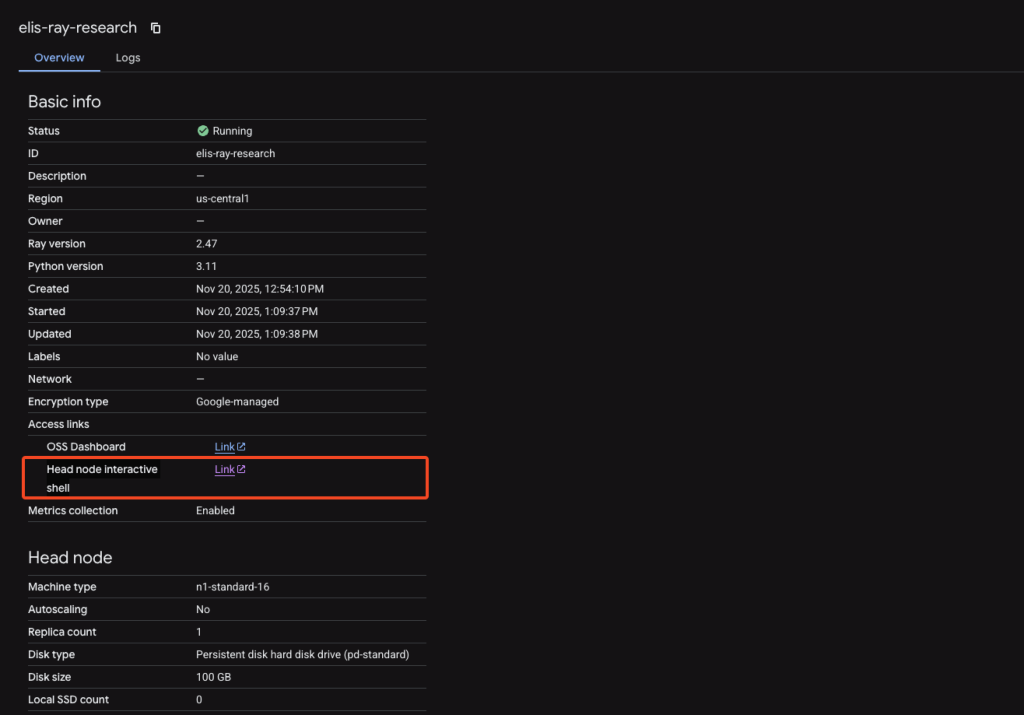
Regardless of having read-only viewer permissions, attackers can click on the “Head node interactive shell” hyperlink within the console to acquire a root shell.
From there, they question the metadata service to retrieve the Customized Code Service Agent entry token.
Whereas the token has a restricted IAM operation scope, it grants full management over storage buckets, BigQuery assets, Pub/Sub, and read-only entry throughout the cloud platform.
Organizations utilizing Vertex AI ought to revoke pointless Service Agent permissions utilizing customized roles, flip off head node shells, validate software code earlier than updates, and monitor metadata service accesses via Safety Command Heart.
Observe us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X to Get Immediate Updates and Set GBH as a Most well-liked Supply in Google.

