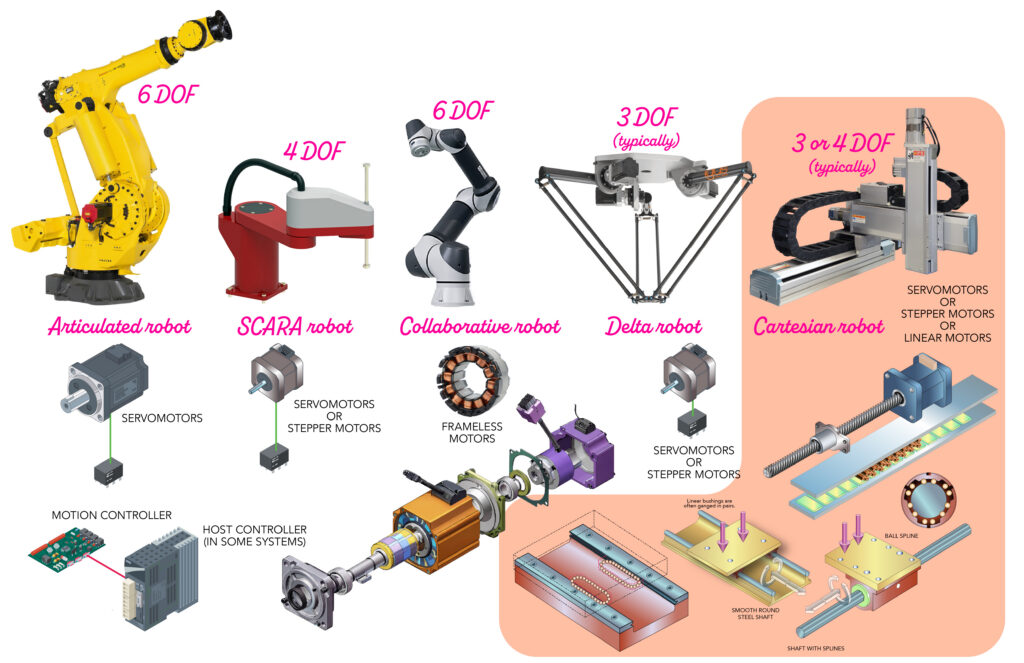
Several types of robots, akin to this cobot arm, depend on totally different motors for exact movement. Supply: Adobe Inventory
Industrial six-axis robots typically combine frameless motors at their axes. Over the previous decade, permanent-magnet brushless servomotors have come to dominate. More and more widespread in six-axis robotic assemblies are frameless and direct-drive variations.
A excessive motor pole depend (with strain-wave gearing) yields excessive torque output and low cogging. Usually finishing such assemblies are an absolute encoder for closed-loop place management and a security (usually closed) holding brake for secure power-off load holding.
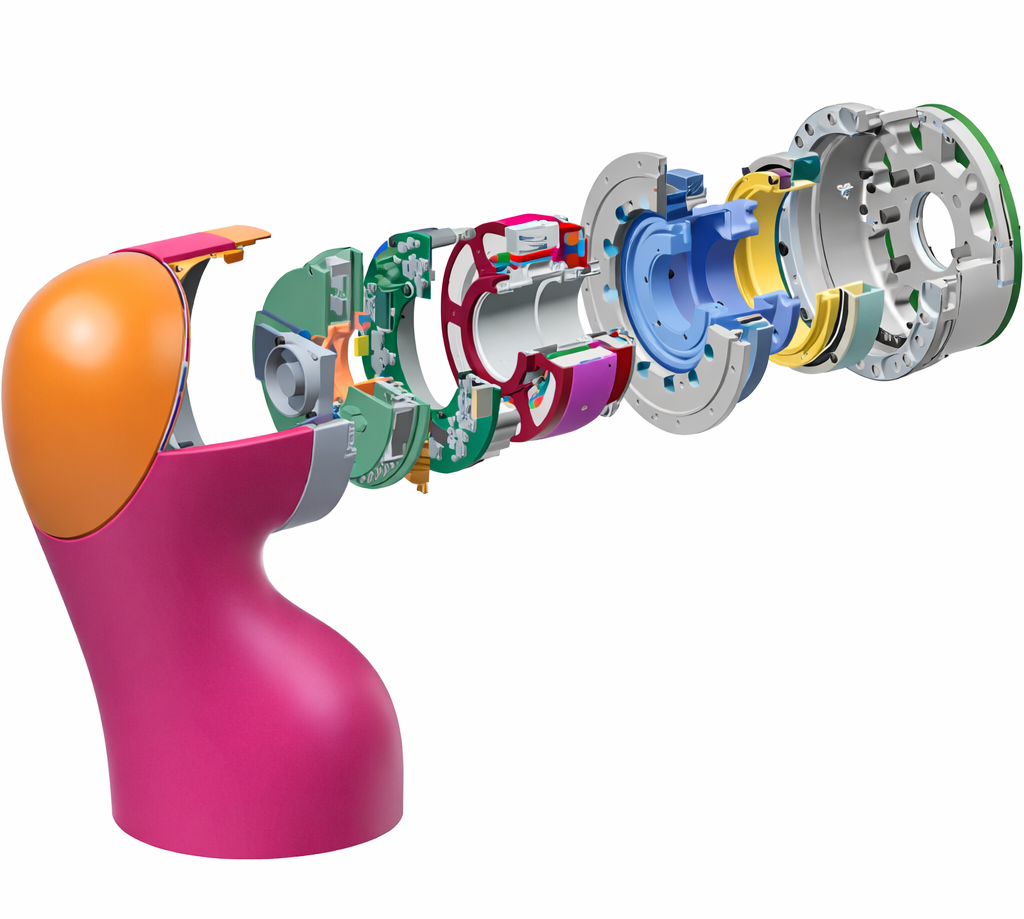
Different torque motors are used with none gearing for direct-drive operation in inspection robots and a few surgical or metrology arms needing true zero-backlash operation.
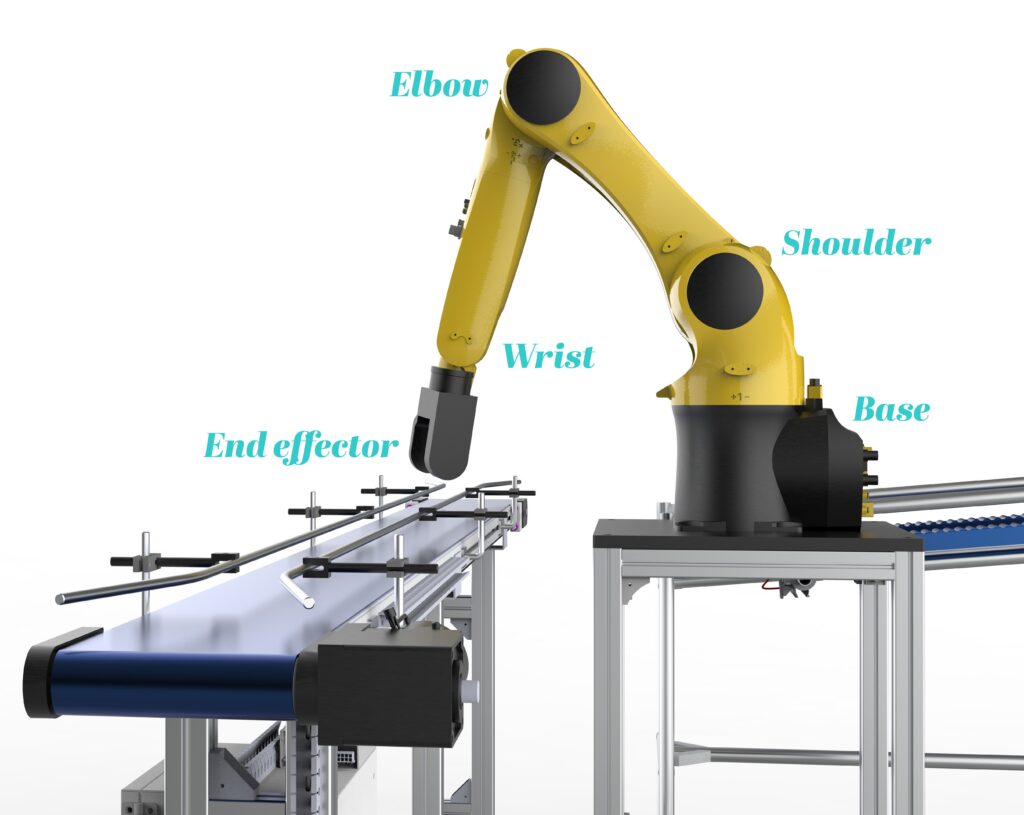
Utilizing the “shoulder-elbow-wrist” analogy to reference levels of freedom, diversifications of field-oriented management together with personalized rotor geometry and windings can tailor robotic shoulder and elbow-joint conduct to arm and payload plenty. Present to windings performing upon a big magnetic airgap impart stiffness and torque density.
In distinction, the motors for wrist roll, pitch, and yaw joints have to be light-weight with low inertia sans vibration. Even right here although, permanent-magnet (PM) AC servomotors nonetheless dominate — although they’re extra more likely to have frameless development and even axial-flux or pancake-type development. Motors in these joints are additionally smaller as a result of complete masses are clearly smaller on the robotic extremity. The excessive torque density of PM motors is vital.
Like articulating six-axis arms, many SCARA robots for horizontal meeting and pick-and-place process additionally combine high-torque AC servomotors on their planar rotary axes for fast accelerations and quick settling. Their vertical Z axes can characteristic servomotor-driven screw drives and even linear motors.
Frameless motors change into widespread as robots converge
Latest years have introduced convergence of articulated industrial robots and collaborative robots as frameless motors have change into extra widespread within the joints of each. Each robotic sorts are additionally making elevated use of machine studying and AI — particularly industry-specific AI and “bodily AI” constructed for a single operate akin to welding, sanding, inspection, or meeting.

The convergence of articulated industrial robots and cobots can also be seeing extra overlap in payload rankings.
Payload mass and second inertia after all consists of that of the moved robotic linkages, finish effector parts, and any precise workpieces being dealt with. With some robots, if a brief derating of velocity, acceleration, and precision is suitable, it is likely to be potential to often exceed rated payload — as long as operations stay decrease than any most payload outlined.
Non-Cartesian robots use a variety of gearing
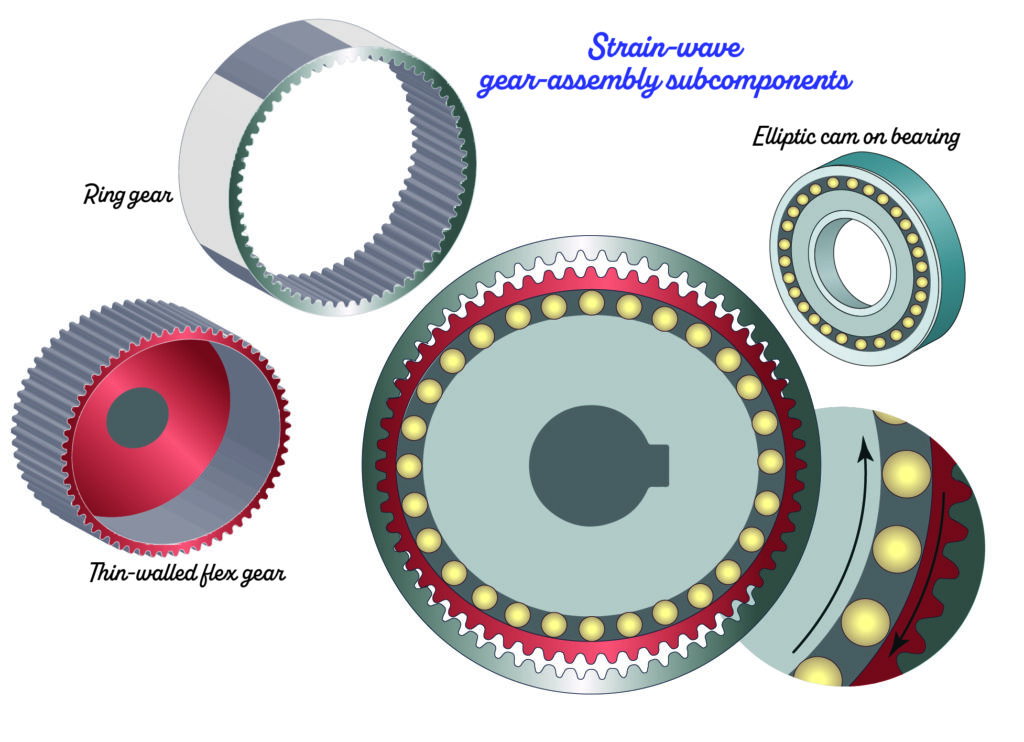
Robotic joints typically have cycloidal gearing in addition to gear units counting on wave-inducing subcomponents having an elliptical or Reuleaux (pronounced “roo-low”) or different polygonal form. Planetary and strain-wave gearing dominate, although proprietary cycloidal programs discover use in specialty robotics.
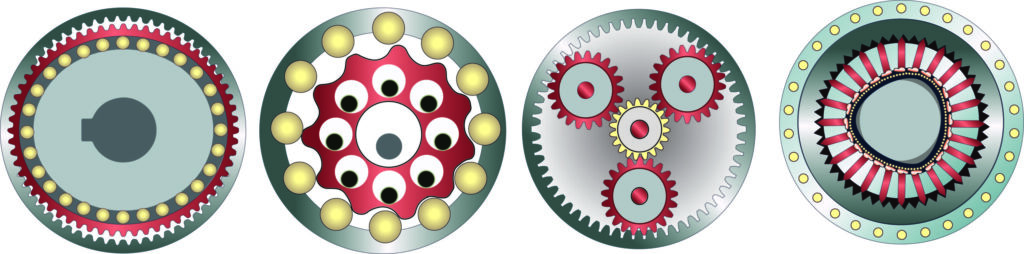
Working example: New FluxWorks magnetic-gearing applied sciences use modulated magnetic fields to exert power with out contact. Keep tuned for extra on this know-how quickly — particularly because it pertains to robotics functions.
One more established gearing possibility for robotics now seeing elevated use has two names:
- Cycloidal gearing.
- Rotary vector or RV gearing as coined by one producer.
At first look, cycloidals resemble trochoidal gearing utilized in sure pumps … however the applied sciences shouldn’t be confused.
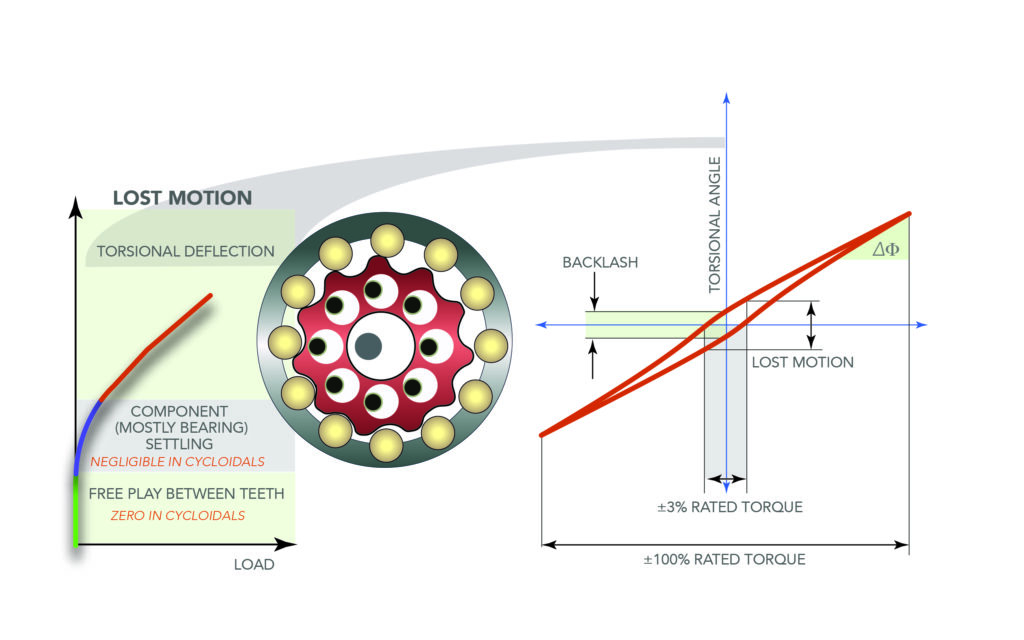
Fast geometry lesson right here … trochoidal and cycloidal gearing consists of components that rotate and hint curves round one other factor. Cycloids traced by a degree on a rolling factor’s circumference embody:
- Epicycloids (for which the factor rolls alongside the surface of a solar gear or different reference element).
- Hypocycloids for which the factor rolls inside a hoop or different reference element.
In distinction, trochoids are traced not by a degree on the rolling factor’s circumference however relatively some level inside or with out.
Technically, planetary units are a form of epicyclic gearing.
For planetary or strain-wave gearing, consultant ratios are 50:1 to 200:1 … although may be decrease at six-axis robots’ wrist joints. Amongst different issues, such gearing boosts acceleration torque for energy density — key for six-axis robotics in addition to SCARA programs for which the meeting is mainly a cantilevered mass.
Suspension modifications seventh-axis gear selection
Beneath now we have gearing examples from GAM Enterprises on every axis’ motor in two robotic arms. Gearing sorts differ for various arm preparations. For instance, essentially the most appropriate gearing within the pinion (and carriage) driving gearmotor of an articulated robotic seventh-axis system partly will depend on the robotic’s orientation in house.
The seventh axis of floor-mount programs typically have a right-angle hypoid gearbox. Mostly “gantry” refers to Cartesian preparations … although suspended six-axis robots additionally qualify. These suspended gantries typically have a helical inline gearbox. Simply to be clear, each assist energy rack-and-pinion units having helical tooth geometries.
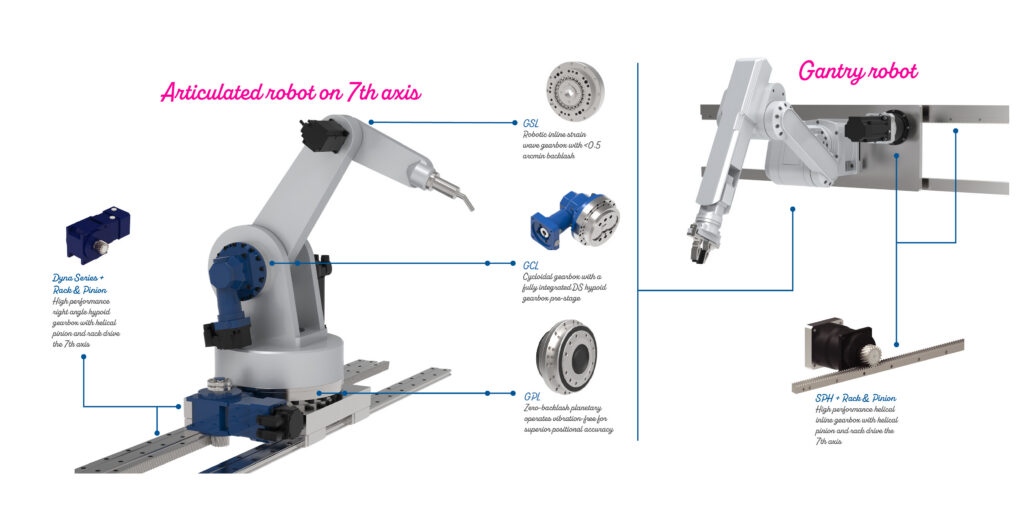
The fitting-angle gearbox for the floor-mounted monitor does a couple of issues: It avoids the robotic’s envelope, an extended drive within the journey course, and awkward mounting.
As an alternative, a right-angle association retains the motor low and tucked alongside the carriage for a stiff and tidy meeting. Hypoid gearing excels on rack-pinion drives due to their excessive torque and ruggedness on reversing axes like this topic to shock masses from regular operation and emergency stops.
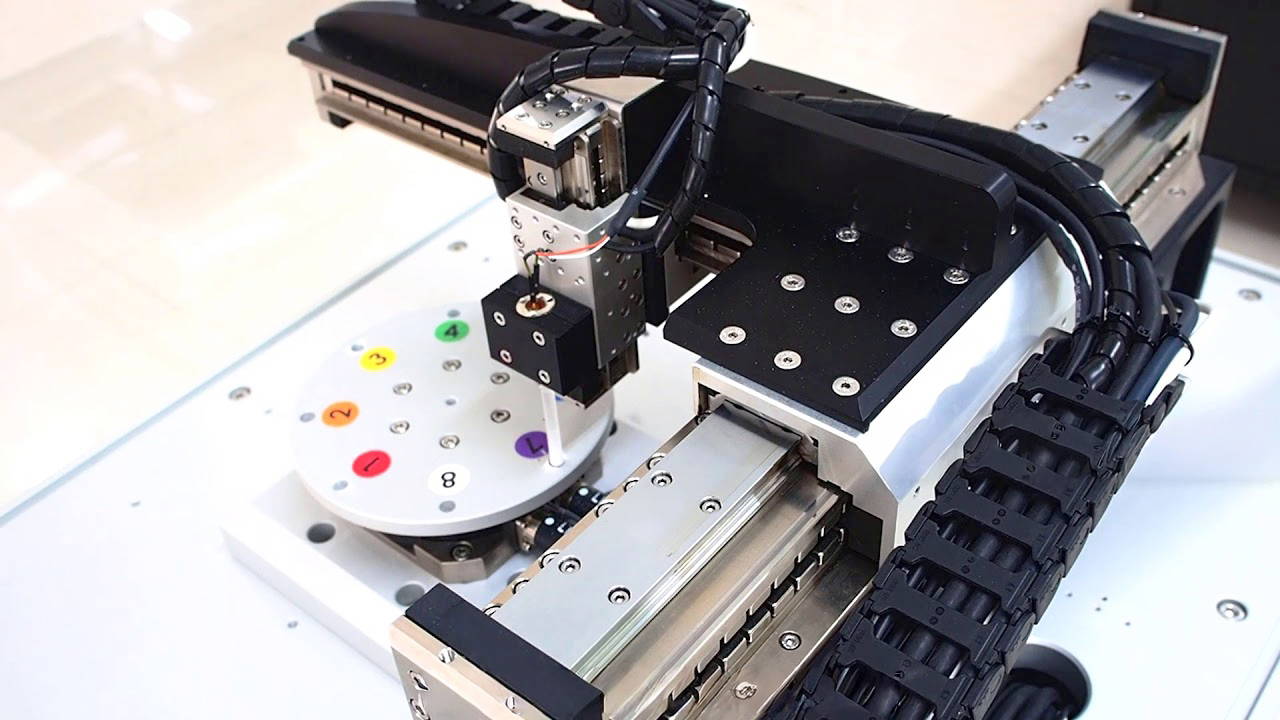
Applied sciences come collectively in miniature robotics
For instance how different parts come collectively, let’s contemplate Chieftek Precision (cpc) S0 miniature robotic arms. These transfer payloads to 0.5 kg with infinite maneuverability from a number of joints.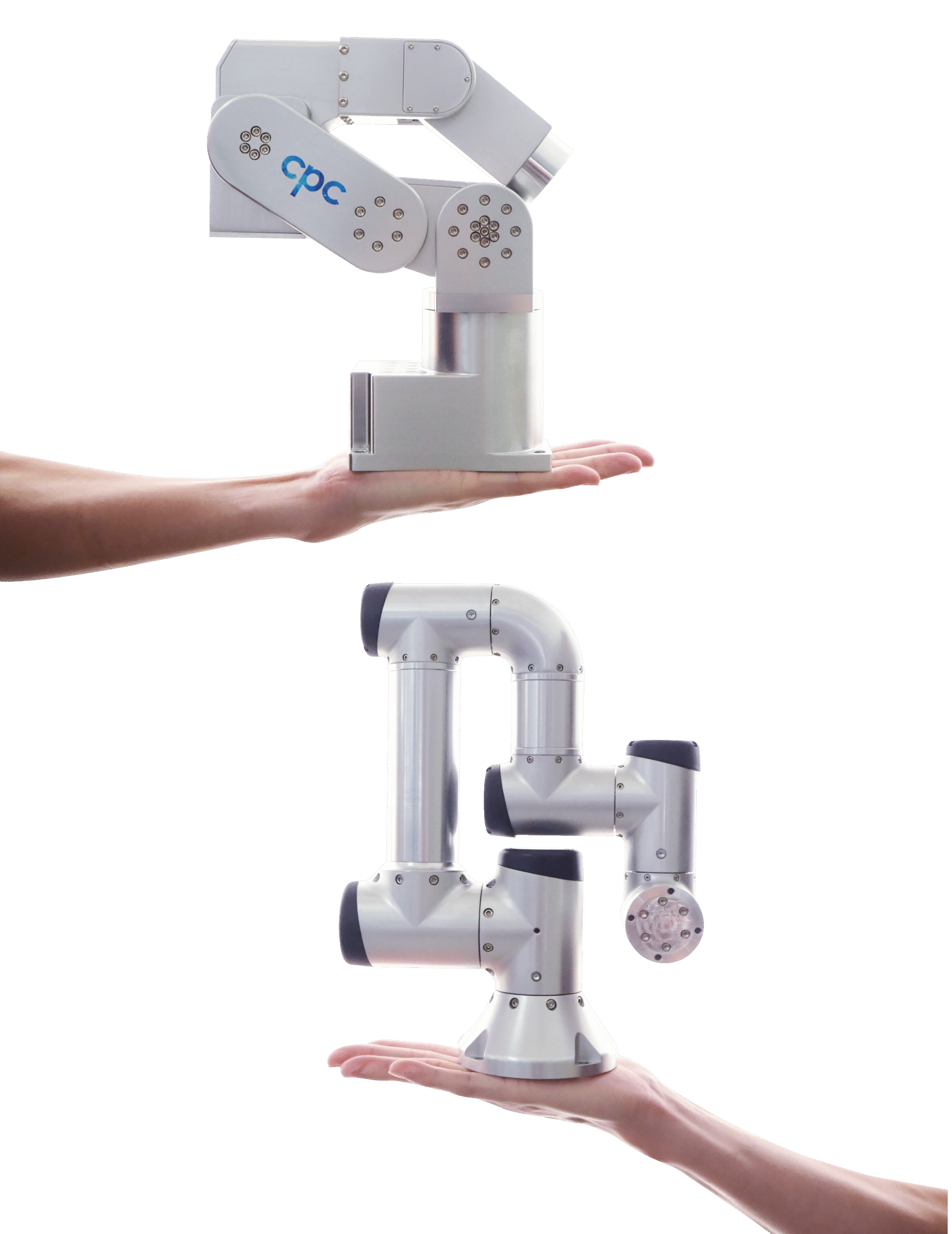
A DB0 model (high proper) presents barely much less maneuverability for increased stiffness and ±5.0-µm repeatability. Each robotic arms combine greater than 200 separate components largely designed and manufactured by Chieftek:
- Customized large-bore frameless motors (accepting 48-V enter) impart movement at every joint.
- Pressure-wave gearing with excessive ratios maximize torque.
- Twin-feedback programs at every axis with an absolute optical encoder and an absolute magnetic encoder sandwiching the gearing to make sure repeatability.
Motor drives with cool-running driver electronics and energy phases full the miniature designs.
Now let’s end up consideration to the one sort of robotic we haven’t detailed but — X-Y-Z Cartesian robots. The cuboid attain of Cartesian gantries or actually any variation are simple to examine. These programs are most fitted the place the top effector can execute its duties in a given orientation inside a aircraft. In actual fact, Cartesians are a most well-liked answer for particularly giant workcells … and for such conditions, typically more economical than a fleet of even very modest SCARA robots. For smaller workcells, Cartesian robots can show a costlier answer.
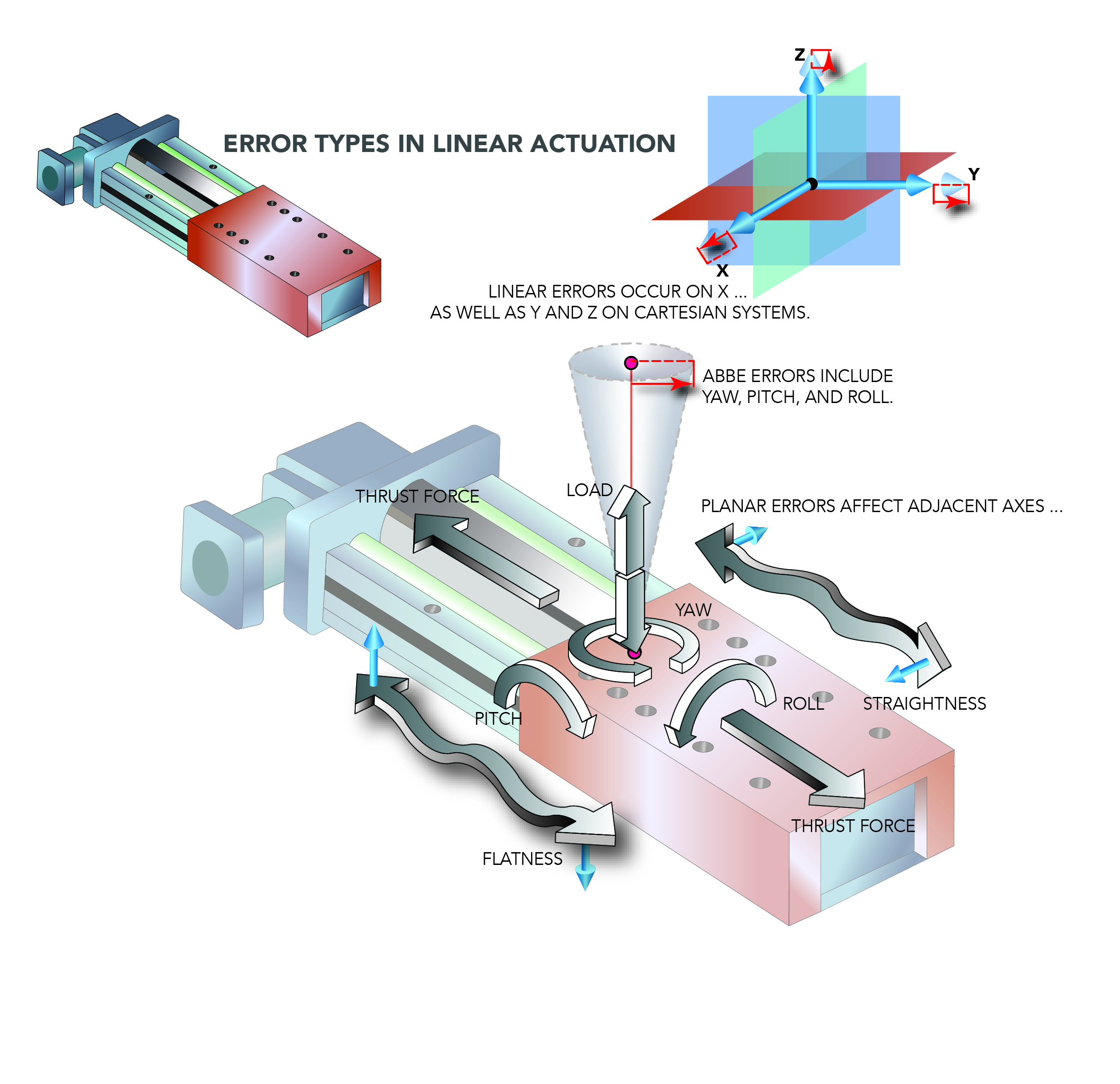
Cartesian-robot axes are by no means completely perpendicular. So, end-effector repeatability about every of axis will depend on that of every drive in addition to the quantity of movement coupling between the axes … with error rising as every axis will get farther from its residence place.
One other consideration: In comparison with that of articulated robotic sorts, the mixing and routing of end-effector provide traces (within the types of cables, hose, carriers, and repair loops) can also be extra concerned.
That stated, a Cartesian robotic personalized to a large-scale manufacturing can fulfill precise necessities like no different possibility. These sorts of conditions justify comparatively excessive upfront prices with long-term efficiencies, output volumes, and scaling of operations.
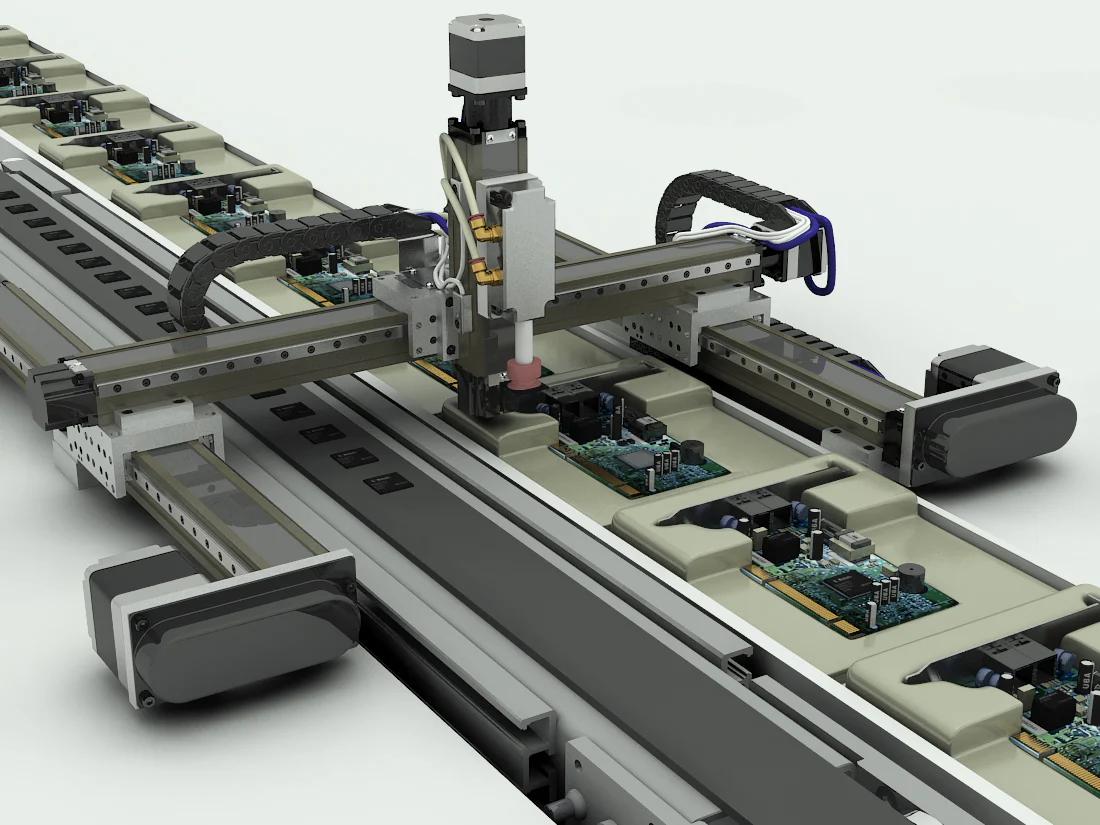
Beneath we see two very totally different Cartesian robots. In each although, modular {hardware} together with sure controllers and communications cut back design complexity.
PBC Linear guides and belt or leadscrew-driven servo or stepper-motorized axes mix to kind customized robotics for half dealing with, vision-based alignment, and different synchronized movement in packaging, meeting, and inspection. The instance right here is an association with stepper motors and screws to automate circuit-board meeting.
Likewise, Chieftek Precision linear guides and linear motors full imaginative and prescient phases, press modules, and laboratory workcells needing fantastic positioning or half transport with extraordinarily excessive rigidity and repeatability.

Editor’s notice: This text is syndicated from The Robotic Report sibling website Design World.

