Chinese language risk actors are weaponizing NFC know-how to steal funds from victims’ financial institution remotely accounts by way of refined Android malware campaigns, with safety researchers figuring out a minimum of $355,000 in fraudulent transactions from a single operation.
Group-IB researchers have uncovered a sprawling cybercrime ecosystem centered round NFC-enabled Android functions that allow criminals to conduct unauthorized tap-to-pay transactions remotely.
Dubbed “Ghost Faucet,” these malicious functions exploit Close to Area Communication know-how to relay fee knowledge from victims’ units to attackers’ units, permitting them to empty financial institution accounts with out bodily entry to fee playing cards.
How the Assault Works
The Ghost Faucet scheme operates by way of a complicated relay mechanism involving two specialised functions: a “reader” put in on the sufferer’s gadget and a “tapper” put in on the attacker’s gadget.
Criminals lure victims by way of smishing (SMS phishing) and vishing (voice phishing) campaigns, convincing them to put in malicious APK information and faucet their financial institution playing cards towards their Android units.
As soon as the sufferer’s card contacts the compromised telephone, the malware captures the NFC fee knowledge and relays it to the attacker’s gadget by way of command-and-control servers.
The cybercriminals then use fraudulently obtained point-of-sale terminals to money out the stolen funds, finishing transactions as if the sufferer’s card have been bodily current.
In different eventualities, criminals preload cell wallets with compromised card particulars and deploy networks of mules throughout the globe to make purchases at bodily retail places utilizing the modified tap-to-pay functions.
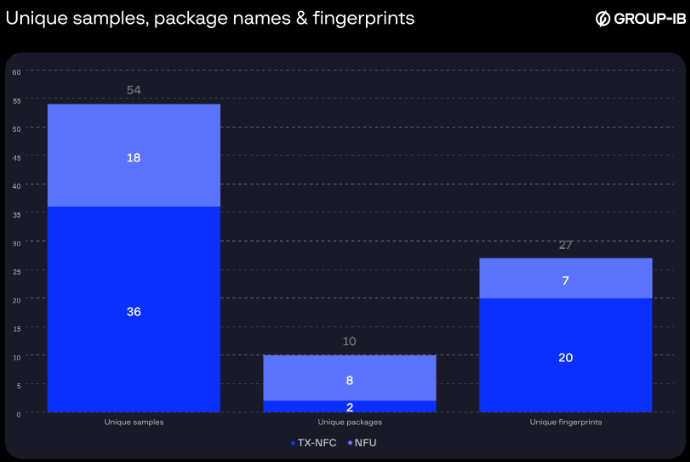
Group-IB’s investigation recognized over 54 APK samples, with some malware variants masquerading as reputable banking functions.
The analysis uncovered three main malware distributors working inside Chinese language cybercrime communities on Telegram: TX-NFC, X-NFC, and NFU Pay.
TX-NFC, the most important vendor recognized, established its Telegram channel in January 2025 and quickly accrued over 21,000 subscribers.
The group gives buyer assist in English and costs its malware from $45 for one-day entry as much as $1,050 for three-month subscriptions.
X-NFC emerged in December 2024 with over 5,000 members, whereas NFU Pay, regardless of having fewer subscribers, has its software redistributed by different distributors below totally different names.
These distributors constantly evolve their choices, with NFU Pay reportedly offering personalized builds for particular nations like Brazil and Italy, together with modifications that take away login necessities to facilitate quicker sufferer concentrating on.
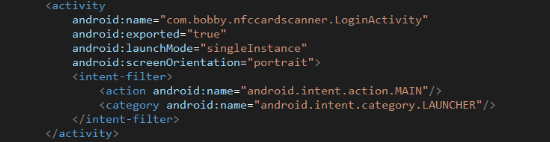
The applying has two exercise parts, the primary of which; “LoginActivity” handles consumer authentication and serves as the applying’s most important entrypoint:
Complementing the malware ecosystem is a thriving marketplace for illegitimately acquired POS terminals.
Oedipus, a Telegram channel affiliated with TX-NFC distributors, overtly advertises POS terminals from monetary establishments throughout the Center East, Africa, and Asia.
Since November 2024, this single operation has processed roughly $355,000 in fraudulent transactions utilizing these stolen terminals.
Authorities worldwide have begun responding to this rising risk. Notable arrests embrace 11 Chinese language nationals apprehended in Knoxville, Tennessee in March 2025 for buying reward playing cards value tens of 1000’s of {dollars} utilizing these Android functions marking the primary arrests of their type in the USA.
In November 2024, Singapore authorities arrested 5 people conducting contactless funds at high-value shops with out bodily playing cards. Czech police, Malaysian authorities, and Chinese language legislation enforcement have additionally made arrests associated to those NFC relay assaults.
The Visa Fee Ecosystem Threat and Management group’s Spring 2025 Biannual Threats Report particularly highlighted the continued use of NFC-enabled malicious functions for relay fraud, whereas Credit score China issued advisories detailing instances the place victims misplaced a minimum of $13,000 to those schemes.
Technical Evaluation
Safety researchers analyzing the malware found that functions like TX-NFC are obfuscated and packed utilizing 360 Jiagu, a Chinese language industrial packer.
Primarily based on Group-IB Fraud Safety knowledge tracked from Might 2024 to December 2025, we will observe a gentle enhance within the detection of tap-to-pay malware samples.
The malware requests important permissions together with NFC {hardware} entry, web connectivity, and foreground service capabilities to keep up persistence even when customers aren’t actively utilizing their units.
The functions particularly goal ISO 14443 contactless fee playing cards and numerous NFC tag varieties.
Upon discovering an NFC-enabled fee card, the malware sends the “2PAY.SYS.DDF01” command to provoke communication with the Proximity Fee System Atmosphere, storing obtainable software identifiers earlier than relaying all knowledge by way of WebSocket providers to the attackers’ command-and-control infrastructure.
Code evaluation revealed that some variants are primarily based on NFCProxy, an open-source mission obtainable on GitHub, demonstrating how cybercriminals adapt reputable applied sciences for malicious functions.
Observe us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X to Get On the spot Updates and Set GBH as a Most popular Supply in Google.

