An ongoing wave of phishing campaigns exploiting pretend assembly invitations from fashionable video conferencing platforms, together with Zoom, Microsoft Groups, and Google Meet.
The assaults use social engineering to lure company customers into downloading malicious “software program updates,” that are, in actuality, digitally signed distant monitoring and administration (RMM) instruments that grant attackers full distant entry to victims’ programs.
These phishing operations depend on trusted collaboration platforms which have turn out to be indispensable in hybrid and distant work environments.
The attackers impersonate company communication channels by distributing convincing e mail invitations that mimic professional assembly notifications.
Recipients are prompted to hitch a gathering or confirm an invitation via misleading hyperlinks hosted on typo-squatted domains resembling zoom-meet.us or teams-updates.internet, which carefully resemble professional company providers.
Upon clicking the pretend hyperlink, victims are redirected to a extremely convincing phishing web page resembling the genuine login or assembly display screen of platforms like Google Meet, Microsoft Groups, or Zoom.
To extend credibility, the phishing pages carefully mimic professional pages, typically displaying lists of individuals who’ve “joined” the decision.
To strengthen legitimacy, these pages might show simulated participant lists and lively assembly interfaces, creating a way of urgency to “be part of instantly.”
Netskope researchers noticed that these interactive decoys encourage victims to behave shortly with out verifying the authenticity of the web page.
The Hook: The “Obligatory Replace” Lure
As customers try to hitch the pretend assembly, they’re prompted with a warning that their conferencing utility is old-fashioned or incompatible.
A pop-up instructs them to obtain and set up a “essential replace” earlier than becoming a member of. This pretend replace is the assault vector an executable masquerading as a professional software program patch.
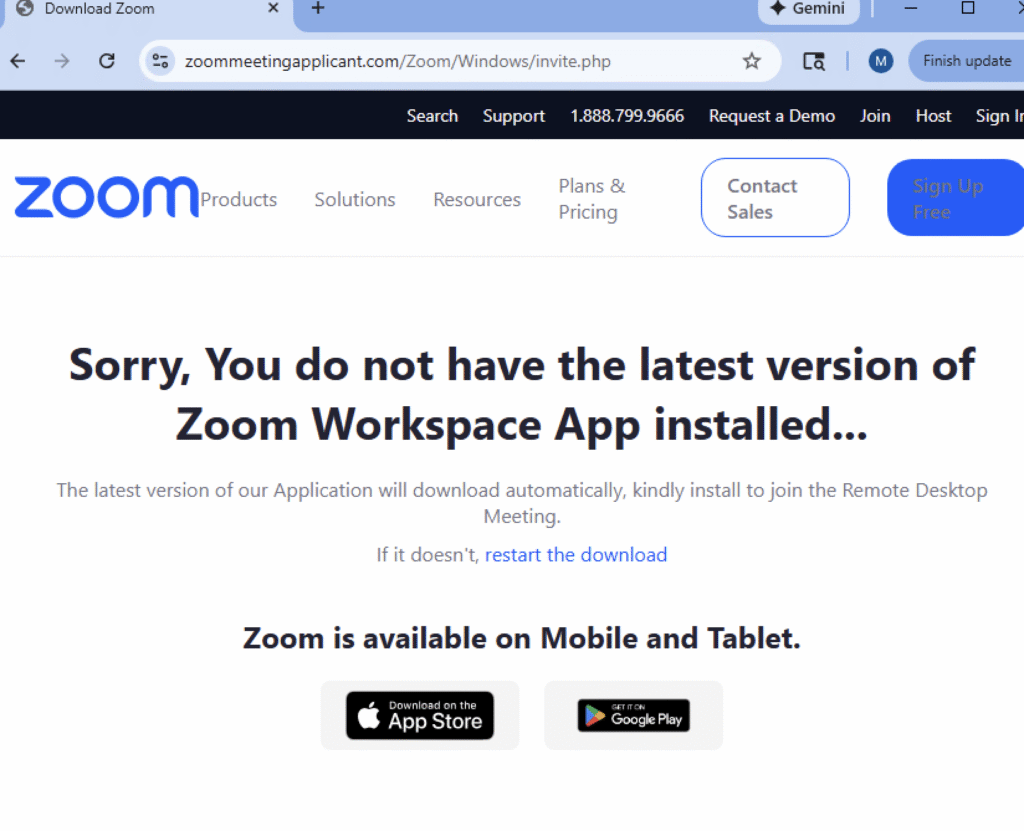
The attackers exploit enterprise urgency and concern of lacking vital conferences, main customers to bypass typical safety warning.
In some circumstances, the phishing websites even embrace on-screen set up directions or progress bars to keep up credibility, guiding victims via the setup technique of the pretend replace in a way in line with professional conferencing instruments.
As soon as executed, the downloaded file installs a professional RMM agent resembling Datto RMM, LogMeIn, or ScreenConnect. Some phishing websites even present steps on the way to “set up” the software program replace.
These instruments, typically pre-approved in enterprise environments, permit distant management, file entry, and system administration. As a result of they’re digitally signed and legit, they’ll simply evade antivirus detections and endpoint safety controls.
Ongoing Risk and Protection Measures
RMM platforms to remotely entry compromised programs, steal company information, transfer laterally, and in extreme circumstances, deploy further payloads resembling ransomware.
The usage of professional, trusted software program minimizes the prospect of detection and gives persistent administrative entry with out triggering conventional risk detection mechanisms.
Netskope Risk Labs warns that these campaigns spotlight how attackers proceed to use belief in collaboration instruments and distant entry software program.
Organizations are suggested to watch using RMM instruments throughout their networks, limit administrative privileges, and educate workers about pretend replace prompts.
IT groups ought to validate that video conferencing updates come solely from official vendor domains and are distributed through safe inner channels.
Observe us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X to Get Prompt Updates and Set GBH as a Most well-liked Supply in Google.

