Databricks is among the main platforms for constructing and executing machine studying notebooks at scale. It combines Apache Spark capabilities with a notebook-preferring interface, experiment monitoring, and built-in knowledge tooling. Right here on this article, I’ll information you thru the method of internet hosting your ML pocket book in Databricks step-by-step. Databricks provides a number of plans, however for this text, I’ll be utilizing the Free Version, as it’s appropriate for studying, testing, and small initiatives.
Understanding Databricks Plans
Earlier than we get began, let’s simply shortly undergo all of the Databricks plans which are obtainable.
1. Free Version
The Free Version (beforehand Neighborhood Version) is the best technique to start.
You may join at databricks.com/study/free-edition.
It has:
- A single-user workspace
- Entry to a small compute cluster
- Assist for Python, SQL, and Scala
- MLflow integration for experiment monitoring
It’s completely free and is in a hosted setting. The largest drawbacks are that clusters timeout after an idle time, sources are restricted, and a few enterprise capabilities are turned off. Nonetheless, it’s supreme for brand new customers or customers attempting Databricks for the primary time.
2. Normal Plan
The Normal plan is good for small groups.
It supplies further workspace collaboration, bigger compute clusters, and integration with your individual cloud storage (resembling AWS or Azure Knowledge Lake).
This stage means that you can hook up with your knowledge warehouse and manually scale up your compute when required.
3. Premium Plan
The Premium plan introduces security measures, role-based entry management (RBAC), and compliance.
It’s typical of mid-size groups that require person administration, audit logging, and integration with enterprise identification methods.
4. Enterprise / Skilled Plan
The Enterprise or Skilled plan (relying in your cloud supplier) contains all that the Premium plan has, plus extra superior governance capabilities resembling Unity Catalog, Delta Dwell Tables, jobs scheduled robotically, and autoscaling.
That is usually utilized in manufacturing environments with a number of groups working workloads at scale. For this tutorial, I’ll be utilizing the Databricks Free Version.
Palms-on
You should use it to check out Databricks free of charge and see the way it works.
Right here’s how one can comply with alongside.
Step 1: Signal Up for Databricks Free Version
- Join together with your e mail, Google, or Microsoft account.
- After you check in, Databricks will robotically create a workspace for you.
The dashboard that you’re taking a look at is your command middle. You may management notebooks, clusters, and knowledge all from right here.
No native set up is required.
Step 2: Create a Compute Cluster
Databricks executes code in opposition to a cluster, a managed compute setting. You require one to run your pocket book.
- Within the sidebar, navigate to Compute.
- Click on Create Compute (or Create Cluster).
- Identify your cluster.
- Select the default runtime (ideally Databricks Runtime for Machine Studying).
- Click on Create and look forward to it to grow to be Working.
When the standing is Working, you’re able to mount your pocket book.
Within the Free Version, clusters can robotically shut down after inactivity. You may restart them everytime you need.
Step 3: Import or Create a Pocket book
You should use your individual ML pocket book or create a brand new one from scratch.
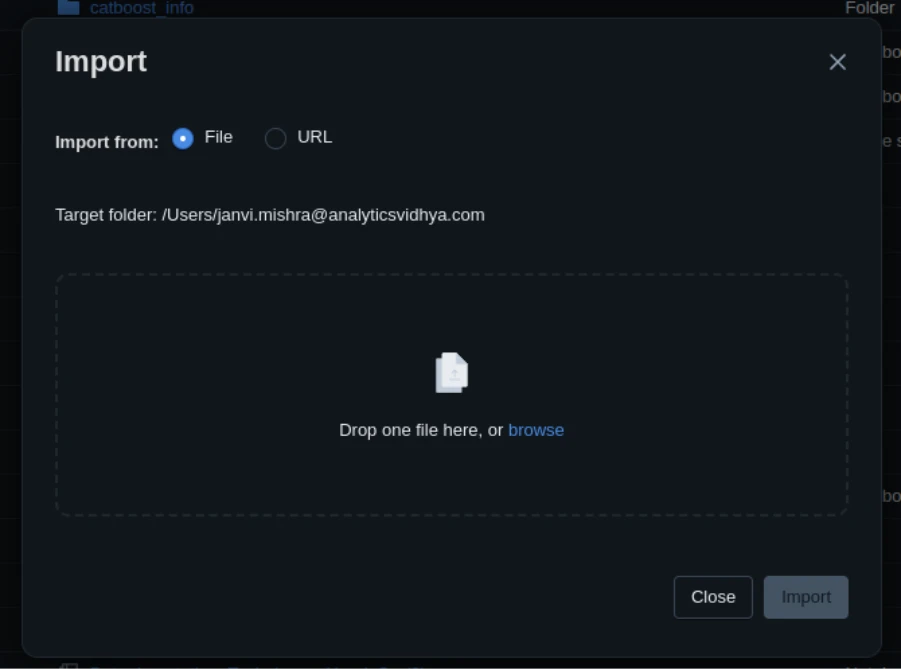
To import a pocket book:
- Go to Workspace.
- Choose the dropdown beside your folder → Import → File.
- Add your .ipynb or .py file.
To create a brand new one:
- Click on on Create → Pocket book.
After creating, bind the pocket book to your working cluster (seek for the dropdown on the prime).
Step 4: Set up Dependencies
In case your pocket book relies on libraries resembling scikit-learn, pandas, or xgboost, set up them inside the pocket book.
Use:
%pip set up scikit-learn pandas xgboost matplotlib 
Databricks may restart the setting after the set up; that’s okay.
Observe: Chances are you’ll must restart the kernel utilizing %restart_python or dbutils.library.restartPython() to make use of up to date packages.
You may set up from a necessities.txt file too:
%pip set up -r necessities.txt To confirm the setup:
import sklearn, sys
print(sys.model)
print(sklearn.__version__) Step 5: Run the Pocket book
Now you can execute your code.
Every cell runs on the Databricks cluster.
- Press Shift + Enter to run a single cell.
- Press Run All to run the entire pocket book.
You’ll get the outputs equally to these in Jupyter.
In case your pocket book has giant knowledge operations, Databricks processes them by way of Spark robotically, even within the free plan.
You may monitor useful resource utilization and job progress within the Spark UI (obtainable below the cluster particulars).
Step 6: Coding in Databricks
Now that your cluster and setting are arrange, let’s study how one can write and run an ML pocket book in Databricks.
We are going to undergo a full instance, the NPS Regression Tutorial, which makes use of regression modeling to foretell buyer satisfaction (NPS rating).
1: Load and Examine Knowledge
Import your CSV file into your workspace and cargo it with pandas:
from pathlib import Path
import pandas as pd
DATA_PATH = Path("/Workspace/Customers/[email protected]/nps_data_with_missing.csv")
df = pd.read_csv(DATA_PATH)
df.head()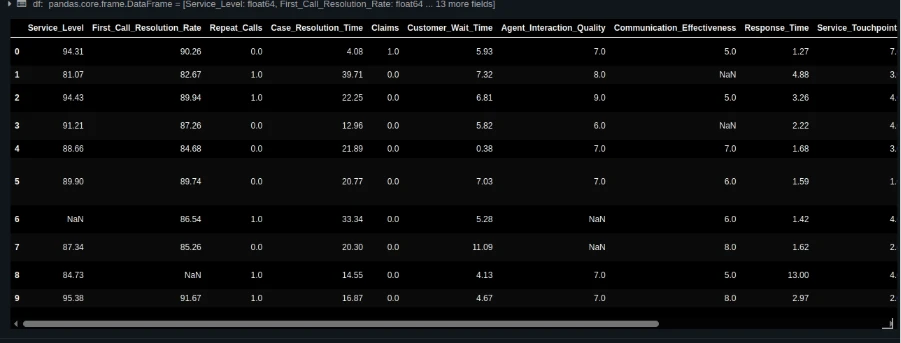
Examine the information:
df.information() 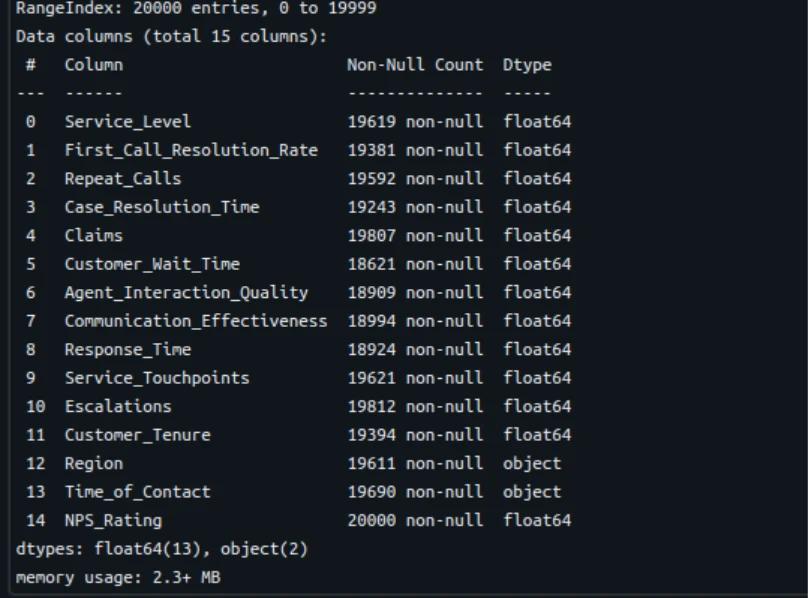
df.describe().T 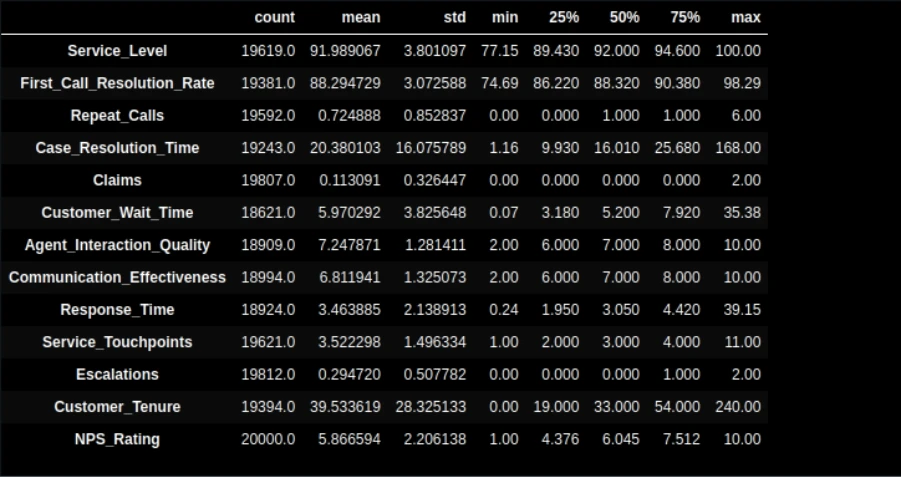
2: Practice/Take a look at Cut up
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
TARGET = "NPS_Rating"
train_df, test_df = train_test_split(df, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
train_df.form, test_df.form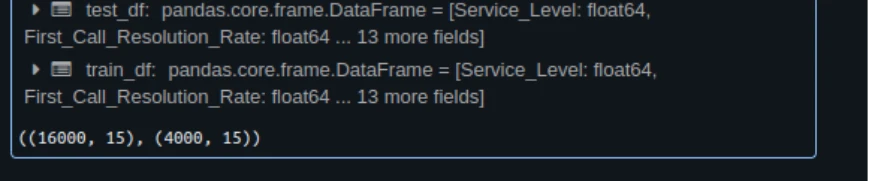
3: Fast EDA
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
sns.histplot(train_df["NPS_Rating"], bins=10, kde=True)
plt.title("Distribution of NPS Rankings")
plt.present() 4: Knowledge Preparation with Pipelines
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer
from sklearn.impute import KNNImputer, SimpleImputer
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, OneHotEncoder
num_cols = train_df.select_dtypes("quantity").columns.drop("NPS_Rating").tolist()
cat_cols = train_df.select_dtypes(embody=["object", "category"]).columns.tolist()
numeric_pipeline = Pipeline([
("imputer", KNNImputer(n_neighbors=5)),
("scaler", StandardScaler())
])
categorical_pipeline = Pipeline([
("imputer", SimpleImputer(strategy="constant", fill_value="Unknown")),
("ohe", OneHotEncoder(handle_unknown="ignore", sparse_output=False))
])
preprocess = ColumnTransformer([
("num", numeric_pipeline, num_cols),
("cat", categorical_pipeline, cat_cols)
]) 5: Practice the Mannequin
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score, mean_squared_error
lin_pipeline = Pipeline([
("preprocess", preprocess),
("model", LinearRegression())
])
lin_pipeline.match(train_df.drop(columns=["NPS_Rating"]), train_df["NPS_Rating"]) 6: Consider Mannequin Efficiency
y_pred = lin_pipeline.predict(test_df.drop(columns=["NPS_Rating"]))
r2 = r2_score(test_df["NPS_Rating"], y_pred)
rmse = mean_squared_error(test_df["NPS_Rating"], y_pred, squared=False)
print(f"Take a look at R2: {r2:.4f}")
print(f"Take a look at RMSE: {rmse:.4f}") 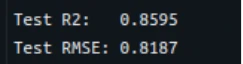
7: Visualize Predictions
plt.scatter(test_df["NPS_Rating"], y_pred, alpha=0.7)
plt.xlabel("Precise NPS")
plt.ylabel("Predicted NPS")
plt.title("Predicted vs Precise NPS Scores")
plt.present() 8: Function Significance
ohe = lin_pipeline.named_steps["preprocess"].named_transformers_["cat"].named_steps["ohe"]
feature_names = num_cols + ohe.get_feature_names_out(cat_cols).tolist()
coefs = lin_pipeline.named_steps["model"].coef_.ravel()
import pandas as pd
imp_df = pd.DataFrame({"function": feature_names, "coefficient": coefs}).sort_values("coefficient", ascending=False)
imp_df.head(10) 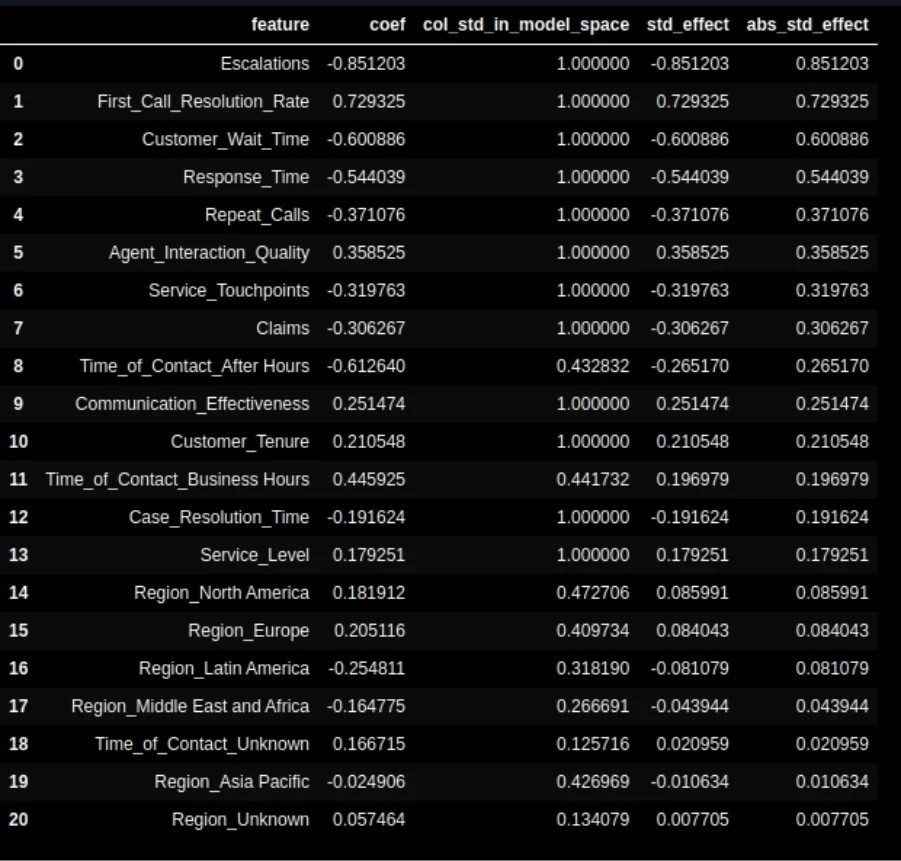
Visualize:
prime = imp_df.head(15)
plt.barh(prime["feature"][::-1], prime["coefficient"][::-1])
plt.xlabel("Coefficient")
plt.title("High Options Influencing NPS")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.present() 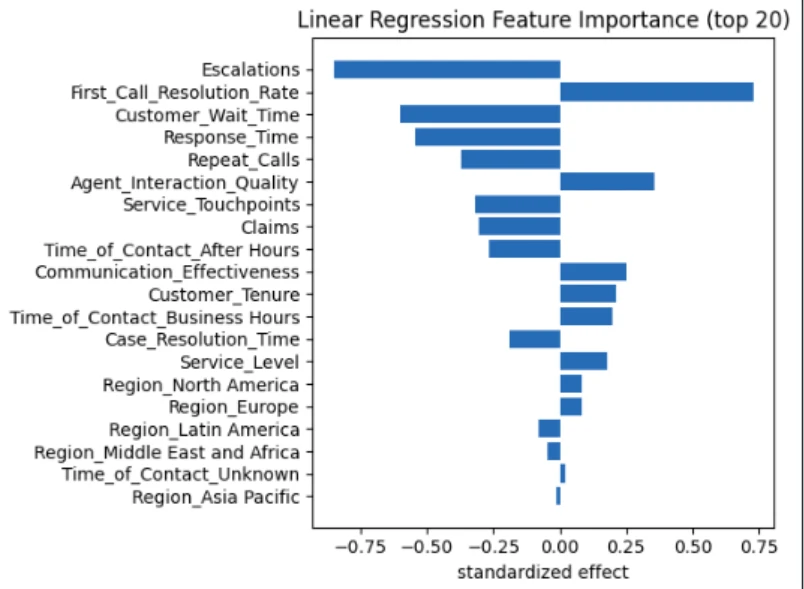
Step 7: Save and Share Your Work
Databricks notebooks robotically save to your workspace.
You may export them to share or save them for a backup.
- Navigate to File → Click on on the three dots after which click on on Obtain
- Choose .ipynb, .dbc, or .html
You can too hyperlink your GitHub repository below Repos for model management.
Issues to Know About Free Version
Free Version is great, however don’t overlook the next:
- Clusters shut down after an idle time (roughly 2 hours).
- Storage capability is restricted.
- Sure enterprise capabilities are unavailable (resembling Delta Dwell Tables and job scheduling).
- It’s not for manufacturing workloads.
Nonetheless, it’s an ideal setting to study ML, attempt Spark, and check fashions.
Conclusion
Databricks makes cloud execution of ML notebooks simple. It requires no native set up or infrastructure. You may start with the Free Version, develop and check your fashions, and improve to a paid plan later in the event you require further energy or collaboration options. Whether or not you’re a scholar, knowledge scientist, or ML engineer, Databricks supplies a seamless journey from prototype to manufacturing.
In case you have not used it earlier than, go to this web site and start working your individual ML notebooks right now.
Continuously Requested Questions
A. Join the Databricks Free Version at databricks.com/study/free-edition. It provides you a single-user workspace, a small compute cluster, and built-in MLflow help.
A. No. The Free Version is totally browser-based. You may create clusters, import notebooks, and run ML code immediately on-line.
A. Use %pip set up library_name inside a pocket book cell. You can too set up from a necessities.txt file utilizing %pip set up -r necessities.txt.
Login to proceed studying and luxuriate in expert-curated content material.

